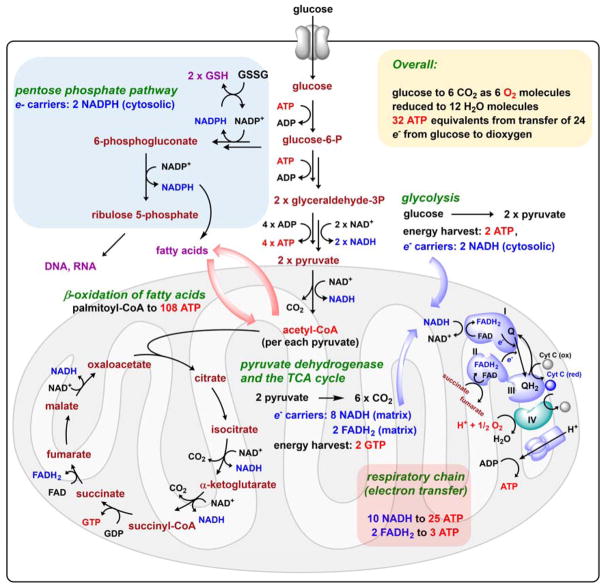
Figure 3.
An overview of cellular glucose metabolism. The coupled pathways of glycolysis, TCA cycle, and electron transport down the membrane respiratory chain summarize removal of 24 electrons from each glucose molecule and ~30 ATP molecules accumulated for each four electron reduction of O2. A second major flux of glucose carbons is via the pentose phosphate pathway, yielding 2 equivalents of NADPH used for fatty acid biosynthesis and to make D-ribose-5-P for nucleic acid biosynthesis. The diagram also notes that complete oxidation of the predominant C16 fatty acyl-CoA, palmityl-CoA to 8 molecules of acetyl-CoA that are run through the TCA cycle and respiratory chain yields ~108 ATPs, emphasizing that saturated fatty acyl chains are energy storage molecules.