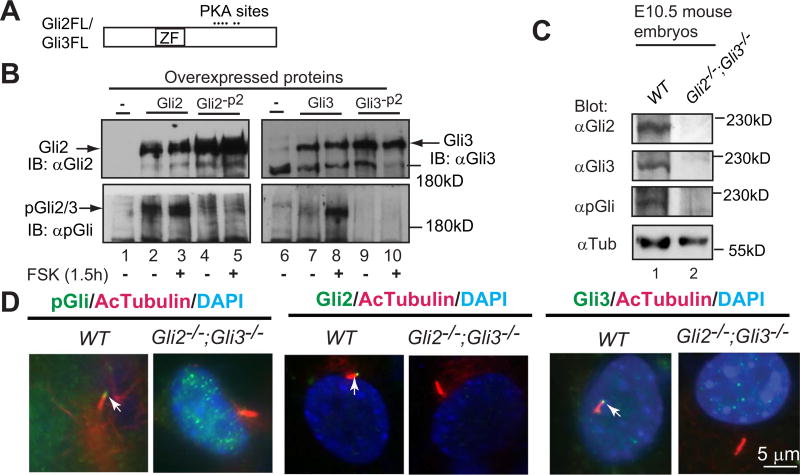
Fig. 1.
A phosphopeptide antibody (pGli) specifically recognizes the phosphorylated Gli2 and Gli3 proteins at the second PKA site. (A) A diagram showing Gli2 and Gli3 proteins with the zinc-finger domain (ZF) and six PKA sites. (B) Immunoblots of overexpressed Gli2, Gli3, and their mutants at the second PKA site (Gli2-P2, Gli3-P2) with Gli2, Gli3, or pGli antibodies. Forskolin (FSK) induces Gli2/Gli3 phosphorylation. (C) Immunoblots of endogenous Gli2, Gli3, and phosphorylated Gli2/Gli3 using protein lysates prepared from wild type (WT) and Gli2;Gli3 double mutant (control) mouse embryos. (D) Gli2, Gli3, and PKA-phosphorylated Gli2 and Gli3 localize to primary cilia. Immunostaining of WT and Gli2;Gli3 double mutant MEFs for the indicated proteins. Note that pGli, Gli2, and Gli3 antibodies are specific, as no signals were detected in the protein lysates and cilia of the mutant cells. AcTubulin, acetylated tubulin, a cilia marker; DAPI, staining for nuclei. These experiments were performed at least two times.