Figure 5.
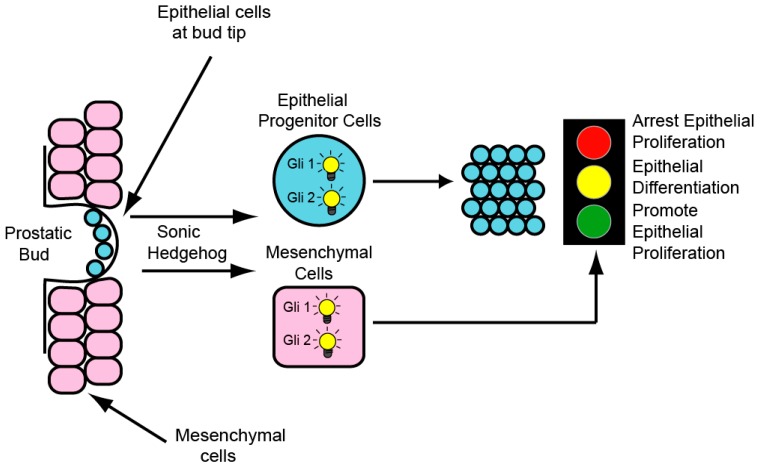
Hh signaling in the developing prostate involves both autocrine and paracrine signaling. Autocrine signaling drives proliferation of (androgen independent) progenitor cells at the bud tip. Paracrine signaling elicits a complex transcriptional response, determined by the stage of development, that exerts a variety of effects on epithelial proliferation and differentiation. In the prenatal prostate, Hh pathway activity drives epithelial proliferation and ductal growth. In the postnatal prostate, Hh pathway activity inhibits epithelial proliferation and ductal growth. Androgen independent progenitor cells generated by autocrine Hh signaling during development are able to survive castration and enable prostate regeneration in response to testosterone supplement.