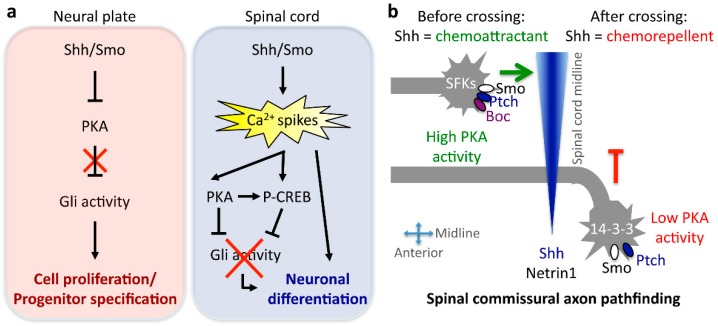
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling conversion during neural development. (a) Canonical Gli signaling is recruited in the developing neural plate, leading to neural stem cell proliferation and neural progenitor specification. The transition from neural plate to spinal cord in Xenopus laevis embryos is accompanied by a switch in Shh signaling from Gli to Ca2+ spike activity dependent, which results in the recruitment of protein kinase A (PKA) and the shutting off of Gli transcriptional activity in the differentiating neuron. (b) Shh action changes when commissural spinal axons cross ventrally the midline from chemoattractant to chemorepellent due to differential, growth cone-localized signaling in mouse embryos. The mediolateral and posteroanterior Shh gradient is represented in blue. P-CREB: phosphorylated cyclic adenosin monophosphate response element-binding protein.