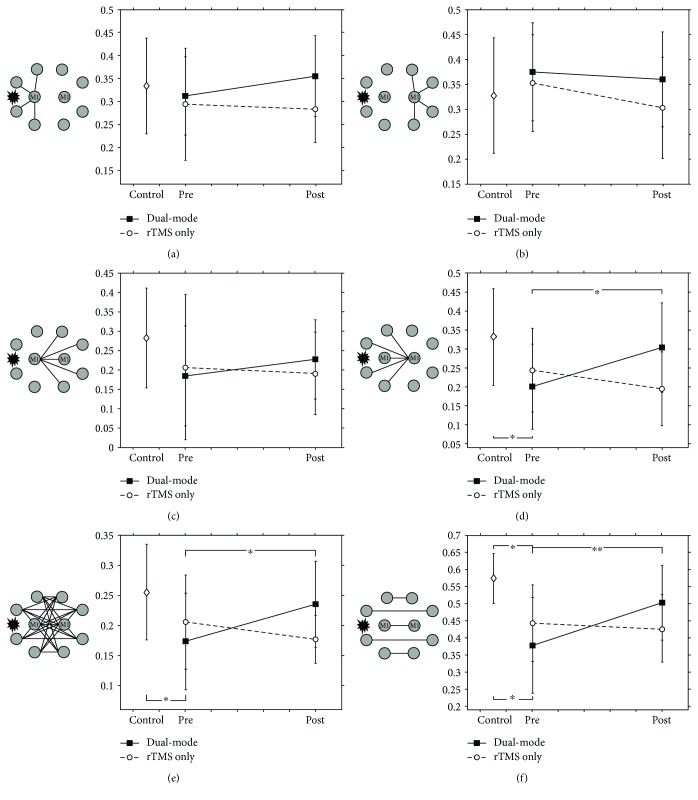
Figure 1.
Altered connectivity caused by stimulation. (a) and (b) are the average strength of the intrahemispheric connectivity of bilateral M1. (c) and (d) are the average strength of the interhemispheric connectivity of bilateral M1. (e) and (f) are the average strength of the overall interhemispheric connectivity and interhemispheric connectivity of the homotopic regions. Interhemispheric connectivity of the contralesional M1 and overall interhemispheric connectivity were significantly increased in the dual-mode stimulation group compared to the rTMS-only group poststimulation (∗ p < 0.05 and ∗∗ p < 0.01, resp.).