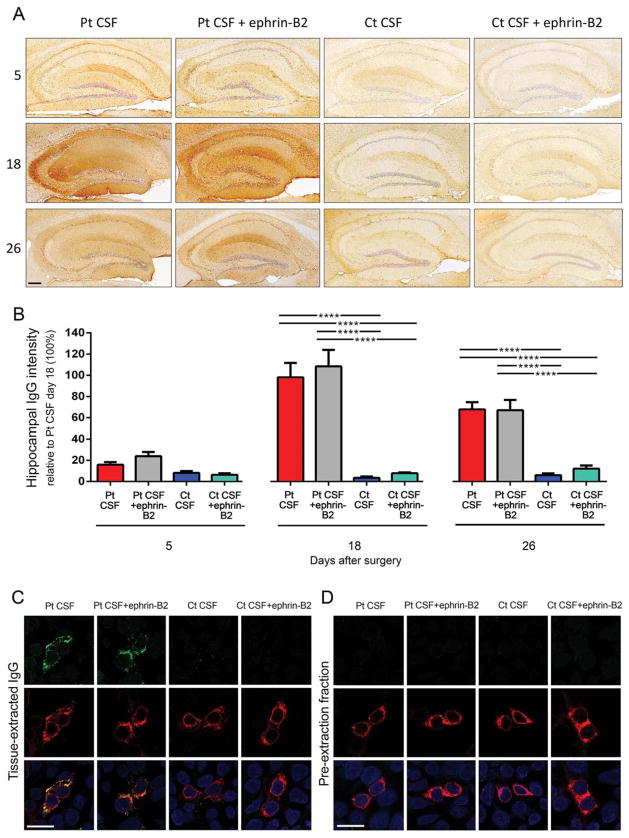
FIGURE 3.
Animals infused with patients’ CSF have a progressive increase of human anti-NMDAR IgG bound to hippocampus that is not altered by ephrin-B2. (A) Immunostaining of human IgG in sagittal hippocampal sections of mice infused with patients’ CSF antibodies (Pt CSF), Pt CSF + ephrin-B2, control CSF (Ct CSF), and Ct CSF + ephrin-B2, sacrificed at the indicated experimental days. In animals infused with patients’ CSF and patients’ CSF + ephrin-B2, there is a gradual increase of IgG immunostaining until day 18, followed by a decrease of immunostaining. Scale bar: A = 200 μm. (B) Quantification of intensity of human IgG immunostaining in hippocampus of mice infused with patients’ CSF (red bars), patients’ CSF + ephrin-B2 (gray bars), control CSF (blue bars), and control CSF + ephrin-B2 (cyan bars) sacrificed at the indicated time points. For all quantifications, mean intensity of IgG immunostaining in the group with the highest value (animals treated with patients’ CSF and sacrificed at day 18) was defined as 100%. All data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. For each time point, 5 animals of each experimental group were examined. Significance of treatment effect was assessed by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA; time points, treatment, and interaction, all p <0.0001), and post-hoc analyses were performed with Bonferroni correction; ****p <0.0001. (C and D) Demonstration that the human IgG in mouse brain has NMDAR specificity: HEK293 cells expressing the GluN1 subunit of the NMDAR immunolabeled with acid-extracted IgG fractions (top row in C) or pre-extraction fractions (top row in D) from hippocampus of mice infused with patients’ CSF antibodies (Pt CSF), Pt CSF + ephrin-B2, control CSF (Ct CSF), or Ct CSF + ephrin-B2 at day 18. The intense reactivity with GluN1-expressing cells was noted in acid-extracted IgG fractions from Pt CSF and Pt CSF + ephrin-B2 groups (C); none of the pre-extraction fractions from any animal group showed GluN1 reactivity (D). The second row in (C) and (D) shows the reactivity with a monoclonal GluN1 antibody, and the third row the colocalization of immunolabeling. Scale bars = 10 μm. Pt CSF (n = 5), Pt CSF + ephrin-B2 (n = 5), Ct CSF (n = 5), and Ct CSF + ephrin-B2 (n = 5). CSF = cerebrospinal fluid; IgG = immunoglobulin G; NMDAR = N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor.