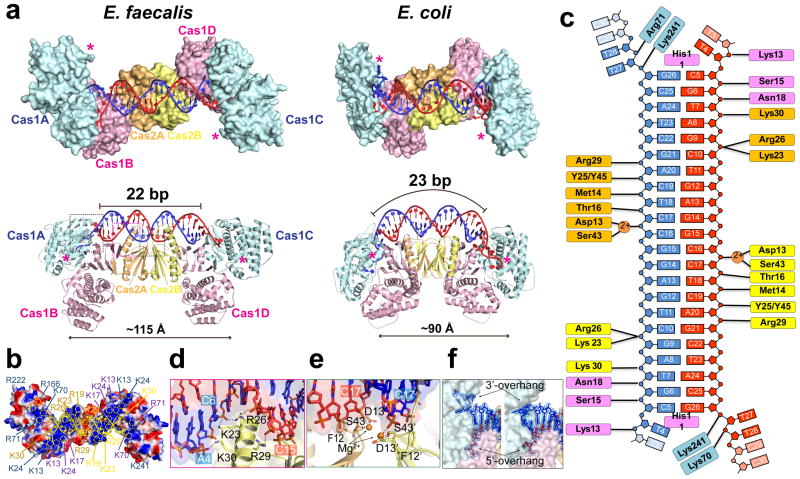
Figure 2. Architectural differences between the 3.25 Å E. fae and E. coli Cas1-Cas2/prespacer structures (PDB: 5DS512) explain their distinct substrate preference.
a, Comparison in the overall dimension, active site distance (in asterisks), and the prespacer duplex curvature. b, Distinct stripes of positive charges on the prespacer-binding surface of EfaCas1-Cas2. c, Interactions diagram between EfaCas1-Cas2 and prespacer. d, An α-helix in EfaCas2 mediates major groove sugarphosphate backbone contacts. e, E13 and S43 in each EfaCas2 coordinate a Mg2+ for DNA backbone contact. f, Prespacer 3′-overhang adopts two distinct conformations.