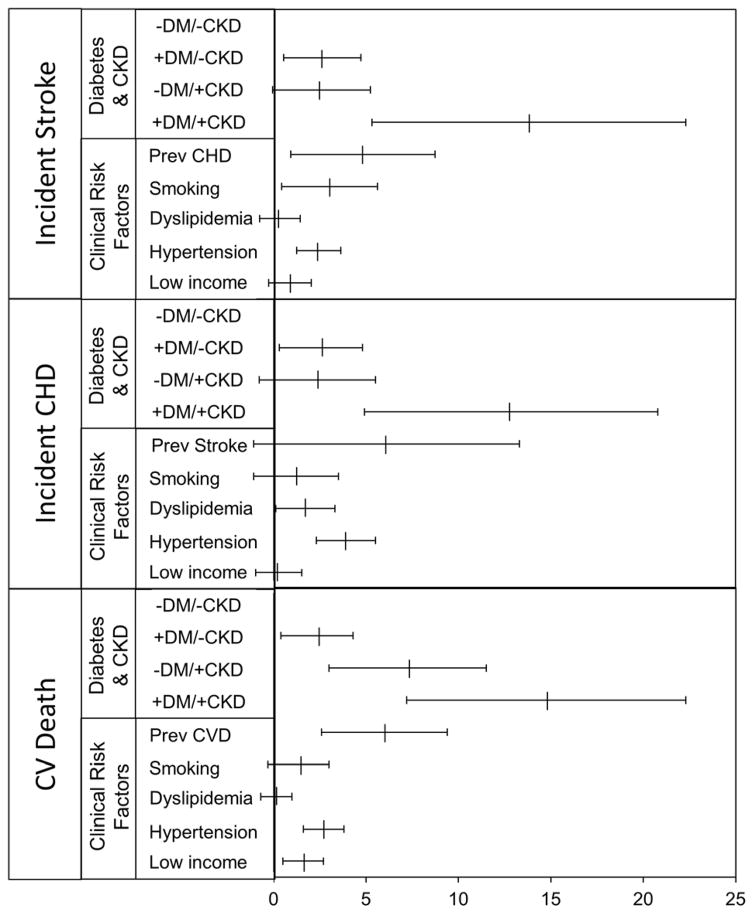
Figure 1. Risk differences for incident stroke, coronary heart disease and cardiovascular mortality (per 1000 person-years) by clinical risk factor in the Jackson Heart Study.
Incidence rates were calculated using Poisson regression. Absolute risk differences were estimated by comparing the incidence rates in each group to that in the reference group (participants with no diabetes or CKD) using Poisson regression and adjusted for age, age2, gender, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoking, and prevalent cardiovascular disease (CVD). Participants with a prior stroke were excluded from the analyses where outcome was incident stroke; participants with prior CHD were excluded from the analyses where outcome was incident CHD. CVD refers to a combination of stroke and CHD.