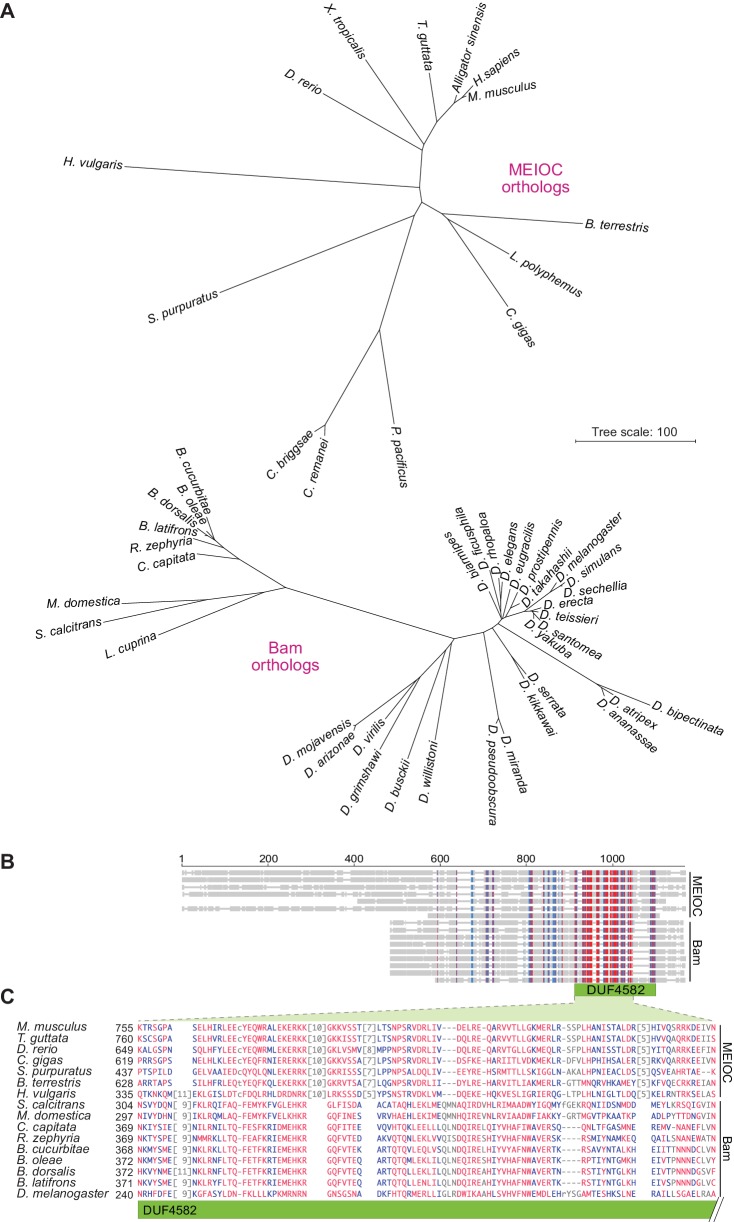
Figure 11. Bam shares distant sequence similarity with MEIOC.
(A) Phylograms based on sequence alignments of MEIOC or Bam orthologs. Sequences were aligned with Clustal Omega and the unrooted neighbor-joining trees were constructed from distances calculated using the scoredist function. Note that the two trees have the same scale, but the MEIOC proteins are from species separated by much greater evolutionary distances. (B and C) Remote sequence similarity between MEIOC and Bam, concentrated across the conserved DUF4582 domain of MEIOC. Sequences were aligned using COBALT (Papadopoulos and Agarwala, 2007). Panel B shows a schematic of the full alignment, with thin gray lines indicating gaps and thick gray lines indicating amino acid sequence. Species are in the same order as panel C, which shows a zoomed-in view of the region of greatest contiguous sequence similarity. Residues aligned across all proteins with no gaps are colored in blue or red according to relative entropy, with red indicating more highly conserved (entropy threshold = 2 bits) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/cobalt/re_cobalt.cgi). Boundaries of DUF4582 are indicated relative to their annotation in the mouse protein. Protein accession numbers are in Supplementary file 3.