Figure 2.
Retinoic Acid Induces Dorsal Spinal Fate in the hESCs
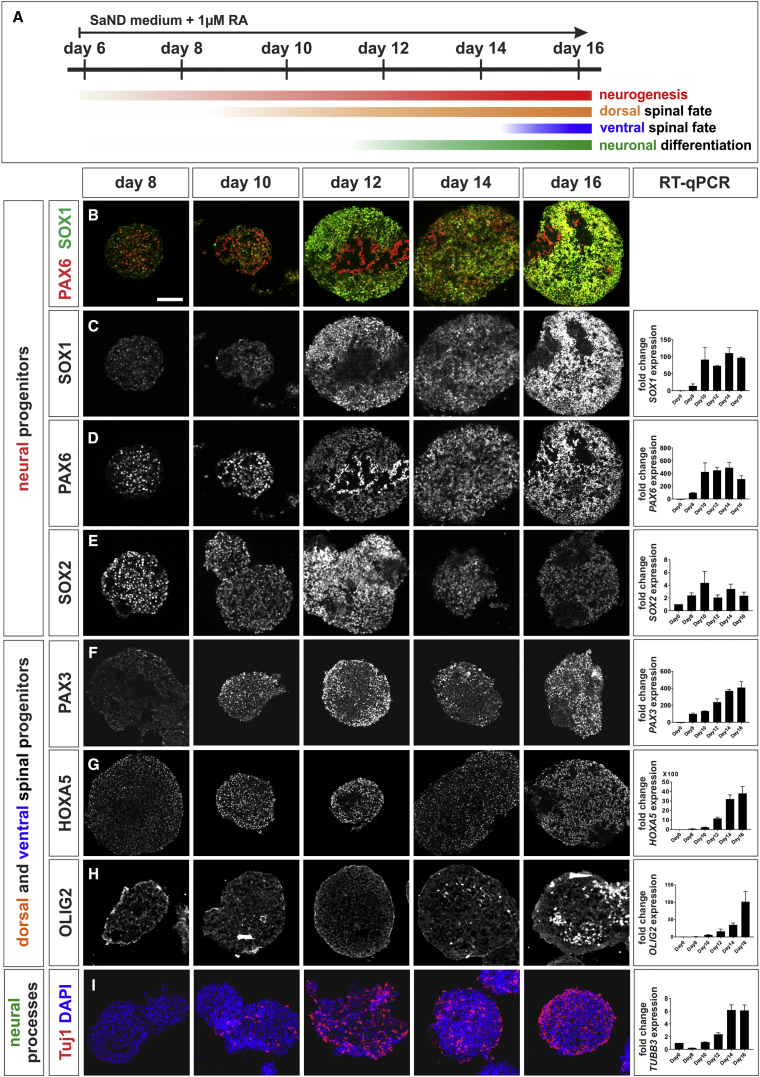
(A) At day 6, the neuralized hESCs were dissociated and allowed to form EBs in SaND medium, supplemented with 1 μM RA. Samples were taken at day 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, and 16 for IHC and RT-qPCR analysis to characterize the early effects of RA on EB identity.
(B–E) RA promotes neural identity: SOX1 (B and C) and PAX6 (B and D) expression increases markedly by day 12. SOX2 starts to decline by day 12, suggesting the onset of neuronal differentiation (E).
(F–H) RA rapidly caudalizes EBs, resulting in a HOXA5+ spinal identity from day 10 (G). EBs also show mixed identities, RA promotes both PAX3+ dorsal fates by day 8 (F) and OLIG2+ ventral fates by day 14 (H).
(I) Longer RA incubation induces neural differentiation, marked by Tuj1 expression in EBs (compare quantification on day 10 and day 12, p < 0.009).
Two biological replicates were performed. Scale bar, 100 μm.