Figure 4.
BMP4 Directs hESCs toward Mechanosensory-dI3 Interneurons
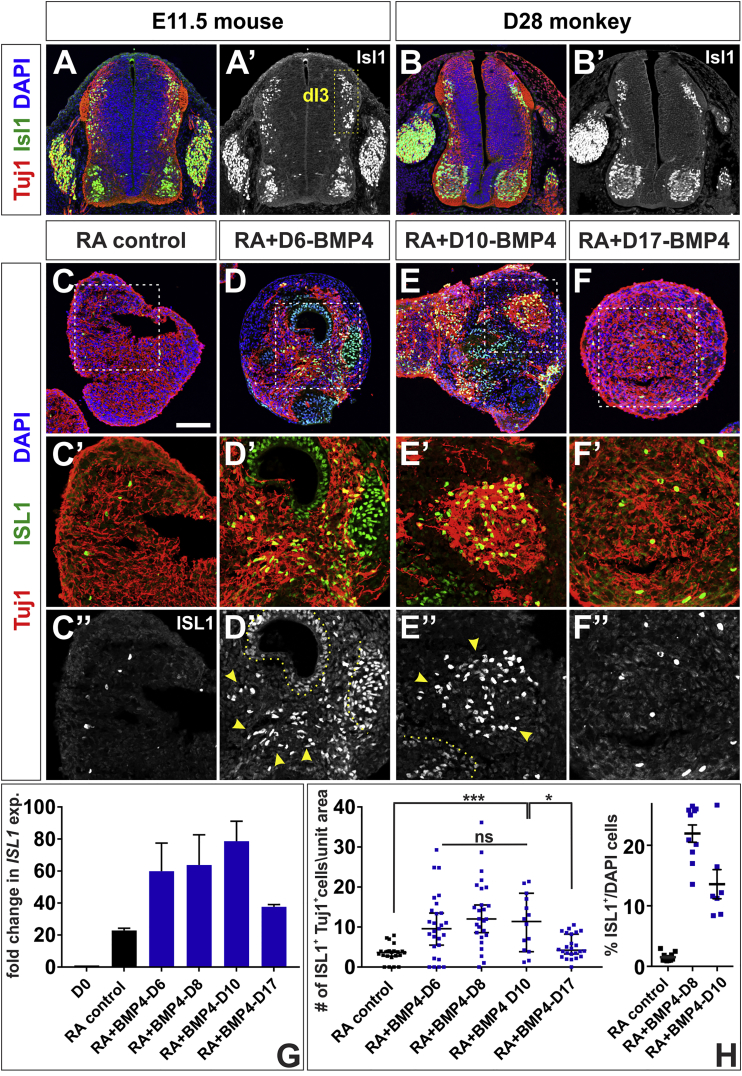
(A and B) Transverse sections of E11.5 mouse lumbar (A) and day 28 Rhesus macaque thoracic (B) embryonic spinal cord labeled with antibodies against β-III tubulin (red, Tuj1) and Isl1 (green). The Isl1+ Tuj1+ mechanosensory dI3 cells are present in the intermediate spinal cord (A, box, A′).
(C–H) Addition of BMP4 at day 6 (D), 8 or 10 (E) resulted in elevated ISL1 expression (G) and significantly increased production of ISL1+ Tuj+ dI3s (arrowheads, D″, E″, quantified in H) compared with RA controls (C″ and H; probability similar to RA control: p < 0.004, BMP4-D6; p < 0.0001, BMP4-D8; p < 0.0008, BMP4-D10); ∼15% of the BMP4-treated cells are ISL1+ (H). However, this effect is lost when BMP4 is added at day 17 (F″, G, and H, probability similar to RA control, p > 0.09). There is no significant difference in ISL1 levels or numbers of ISL1+ Tuj+ dI3s in the BMP4-D6, BMP4-D8 and BMP4-D10 conditions (L, BMP4-D6 versus BMP4-D8 versus BMP4-D10, p > 0.37, one-way ANOVA). Note that not all ISL1+ cells are Tuj1+ (dotted lines, D″, and E″). The region in the white dashed box in (C)–(F) is shown in higher magnification in (C′)–(F′) and (C″)–(F″).
Probability of similarity ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.0005. Six biological replicates were performed with 14–27 EBs quantified. The number of cells was normalized and then scaled according to a unit area (10,000 μm2). Scale bar, 100 μm.