Figure 2. Probe-wise association of alcohol use in the prefrontal cortex.
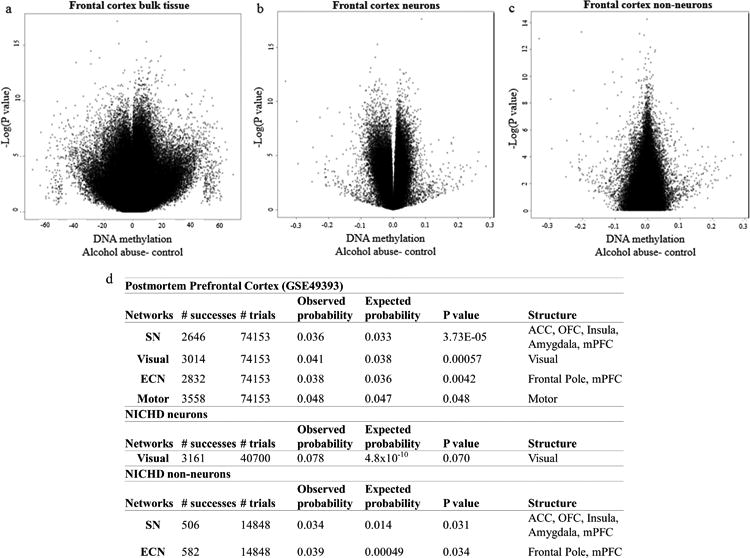
(a) Volcano plot depicting the negative natural log of the p-value of association of alcohol abuse (y-axis) as a function of the beta value (x-axis) from a linear model adjusting for age, sex, and neuronal proportion as estimated by the Cell EpigenoType Specific (CETS) algorithm. Data derived from frontal cortex bulk tissue from GEO dataset GSE49393. Three loci were significant after false discovery rate (FDR) based correction for multiple testing including cg00393248 (MYLK4; β= 9.32 ± 1.516, F= 10.061, df= 5/43, P= 2.23×10-7, FDRP= 0.038), cg19608003 (SLC44A4; β= -13.468 ± 2.011, F= 11.879, df= 5/43, P= 3.54×10-8, FDRP= 0.015), and cg19955284 (β= -19.036 ± 3.122, F= 9.902, df= 5/43, P= 2.64×10-7, FDRP= 0.038). (b) Volcano plot depicting the negative natural log of the p-value of association of alcohol abuse in FACs isolated NeuN positive neuronal nuclei from the NICHD cohort (y-axis) as a function of the beta value (x-axis) from a linear model adjusting for age, sex, race, and Body Mass Index (BMI). In neurons, only cg03982998 (LOC100130331; β= 0.087 ± 0.013, F= 10.487, df= 7/51, P= 2.3×10-8, FDR P= 0.0078) and cg06395265 (ZSWIM1; β= -0.049 ± 0.008, F= 8.967, df= 7/51, P= 2.36×10-7FDR P= 0.041) were significant after correction for multiple testing.(c) Volcano plot depicting the negative natural log of the p-value of association of alcohol abuse in FACs isolated NeuN negative non-neuronal nuclei from the NICHD cohort (y-axis) as a function of the beta value (x-axis) from a linear model adjusting for age, sex, race, and PMI. (d) A table depicting functional connectivity networks significantly over-represented among AUD associated probes from GEO dataset GSE49393 and isolated neuronal and glial nuclei from the NICHD cohort.Structures analyzed included the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), orbitofrontal cortex (OFC), insula, amygdala, visual cortex, motor cortex, frontal pole and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC).
