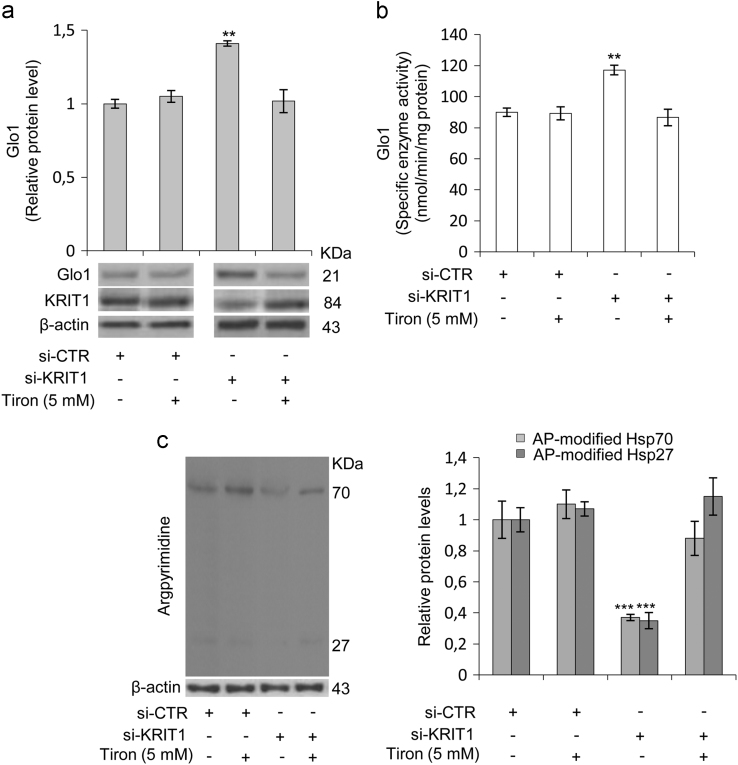
Fig. 3.
KRIT1 silencing in human brain microvascular endothelial cells causes a redox-dependent upregulation of Glyoxalase 1 (Glo1) and downregulation of argpyrimidine (AP) adducts. Human brain microvascular endothelial cells (hBMEC) grown under standard conditions were transfected with either KRIT1-targeting siRNA (si-KRIT1) or a scrambled control (si-CTR). Cells were then either mock-treated or treated with the ROS scavenger Tiron (Tir, 5 mM for 24 h), lysed and analyzed by Western blotting (a,c) and spectrophotometric enzymatic assay (b). a) Representative WB and quantitative histogram of the relative KRIT1 and Glo1 protein expression levels in si-CTR and si-KRIT1 hBMEC cells either mock-treated (−) or treated (+) with Tiron. β-actin was used as internal loading control for WB normalization. The WB bands of Glo1 were quantified by densitometry, and normalized optical density values were expressed as relative protein level units referred to the average value obtained for mock-treated si-CTR samples. b) Glo1 enzyme activity was measured in cytosolic extracts of si-CTR and si-KRIT1 hBMEC cells, either mock-treated (−) or treated (+) with Tiron, according to a spectrophotometric method monitoring the increase in absorbance at 240 nm due to the formation of S-D- lactoylglutathione. Glo1 activity is expressed in milliunits per mg of protein, where one milliunit is the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the formation of 1 nmol of S-D-lactoylglutathione per min under assay conditions. Results represent the mean (± SD) of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. c) Representative WB and quantitative histogram of argpyrimidine (AP) adducts in si-CTR and si-KRIT1 hBMEC cells, either mock-treated (−) or treated (+) with Tiron, as detected using a specific mAb. β-actin was used as internal loading control for WB normalization. Notice treatment of si-KRIT1 hBMEC cells with the antioxidant Tiron rescued the significant increase in Glo1 expression and activity, and decrease in both 70 and 27 kDa AP adducts caused by KRIT1 knockdown.