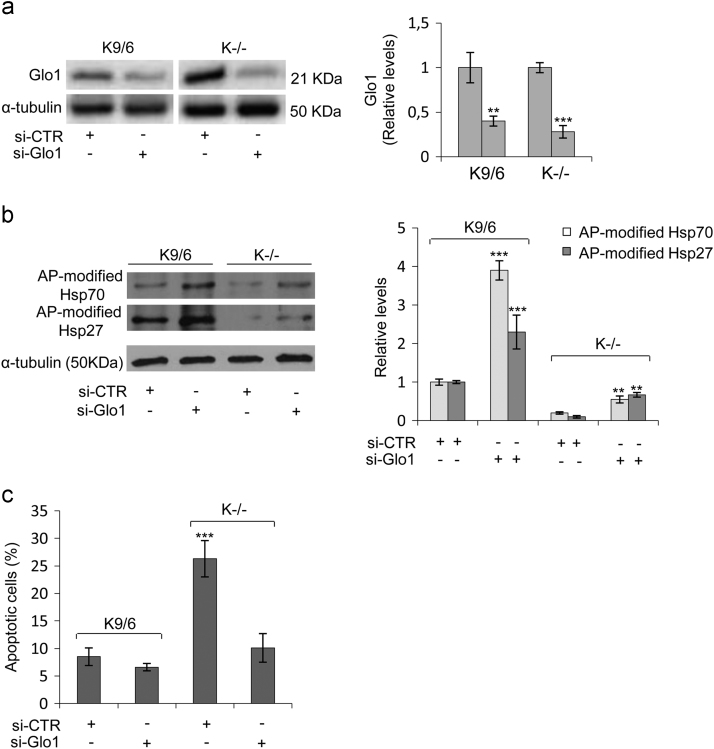
Fig. 5.
The downregulation of AP-modified Hsps and increased apoptosis susceptibility caused by KRIT1 loss-of-function are linked to the upregulation of Glo1. KRIT1−/− (K−/−) and KRIT1−/− re-expressing KRIT1 (K9/6) MEF cells grown to confluence under standard conditions were transiently transfected with either a pool of four siRNAs targeting Glo1 (si-Glo1) or non-targeting siRNAs used as negative control (si-CTR), and Glo1 (a), AP-modified Hsp70 and Hsp27 (b), and apoptosis (c) levels were assayed as described in Section 2. (a,b) Representative Western blots and quantitative histograms of the relative expression levels of Glo1 (a) and argpyrimidine (AP) adducts (b) in K9/6 and K−/− MEF transfected with si-CTR or si-Glo1, as detected using specific antibodies. α-tubulin was used as internal loading control for WB normalization. WB bands were quantified by densitometry, and normalized optical density values were expressed as relative protein level units. The histograms beside their representative Western blots show the mean (± SD) of the densitometric quantification of three independent experiments. (c) Apoptotic cell death evaluated by TUNEL assay in K9/6 and K−/− MEF transfected with si-CTR or si-Glo1. Histograms represent the mean (± SD) of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. Notice that Glo1 silencing induced a significant rescue of both the downregulation of AP-modified Hsp70 and Hsp27 levels, and the increased apoptosis susceptibility associated with KRIT1 loss-of-function.