Fig. 2.
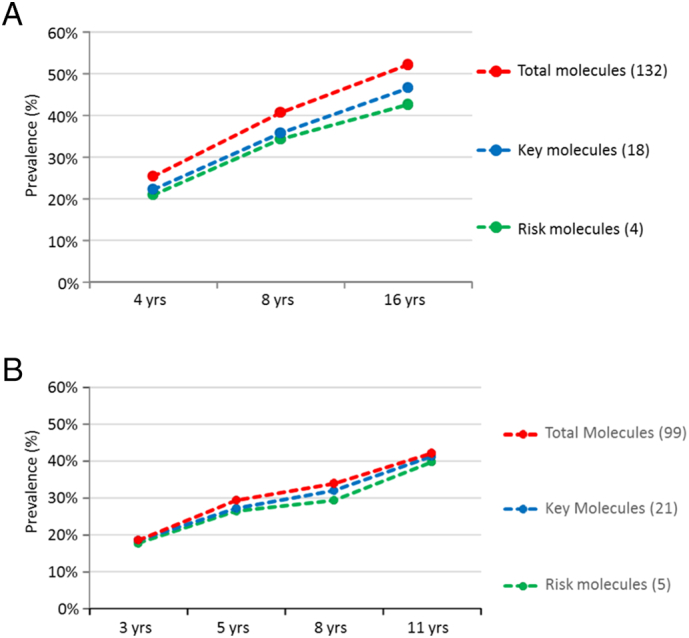
A. (BAMSE). Prevalence of IgE reactivity (%, y-axis) in the population of 786 children at ages 4, 8, 16 years (x-axis) using different sets of molecules at all ages (132), as well as key (18) and risk molecules (4) identified at 4 years. Prevalence indicates IgE reactivity to any of the molecules in each of the three groups. Four risk molecules were identified: Ara h 1 (peanut); Bet v 1 (birch pollen); Fel d 1 (cat) and Phl p 1 (timothy grass pollen). B. (MAAS). Prevalence of IgE reactivity (%, y-axis) in the population of 848 children at ages 3, 5, 8, 11 years (x-axis) using different sets of molecules at all ages (99), as well as key (21) and risk molecules (5) identified at 3 years. Prevalence indicates IgE reactivity to any of the molecules in each of the three groups. Five risk molecules were identified: Der p 1 (Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus); Der f 2 (Dermatophagoides farinae), Phl p 1 and Phl p 5 (timothy grass pollen), and Fel d 1 (cat).
