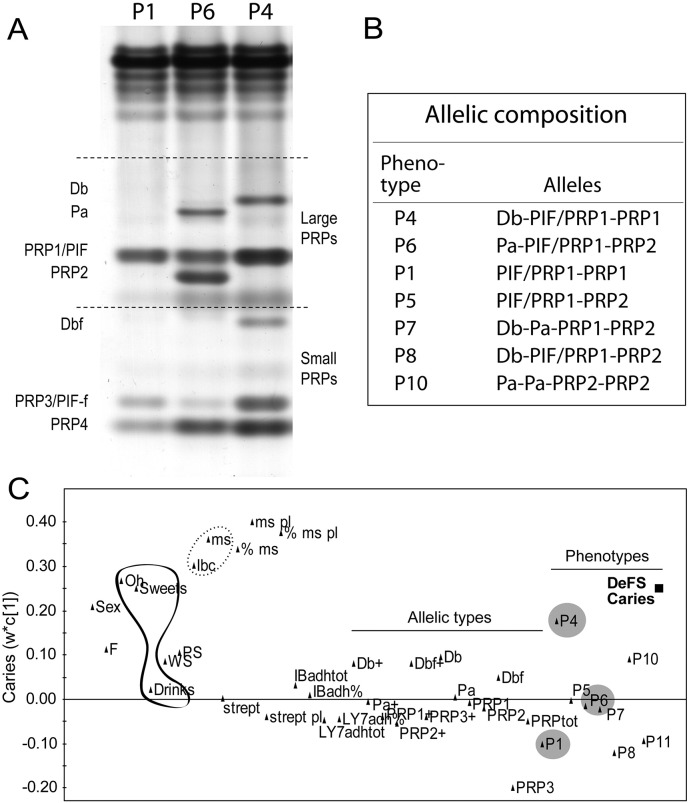
Fig. 1.
Acidic PRP phenotypes, their allelic composition and association with baseline caries. (AB) Allelic types and amounts of mixed acidic PRP phenotypes P1-P10 from gel electrophoresis of parotid saliva in 218 12-year-old children. (C) PLS loading plot showing the association of P4, P6 and P1 children (grey circles) and traditional risk factors (S. mutans, lactobacilli > oral hygiene > sweets >> drinks) with baseline caries in children with Swedish ethnicity (n = 185); Sex = 0 boys, 1 girls; F = extra fluoride; Oh = oral hygiene; WS = whole saliva flow; PS = parotid saliva flow; lbc = lactobacilli in saliva; ms, ms pl, % ms and % ms pl = S. mutans and % of total streptococci in saliva and plaque; strept, strept pl = total streptococcal in saliva, plaque; IBadh = S. mutans adhesion, % and tot; LY7adh = A. oris adhesion, % and tot); Db + etc. and Db etc. = qualitative, +, and quantitative acidic PRP variants from electrophoresis; PRPtot = total amounts of PRPs; P1, P4 etc. = mixed acidic PRP phenotypes from electrophoresis.