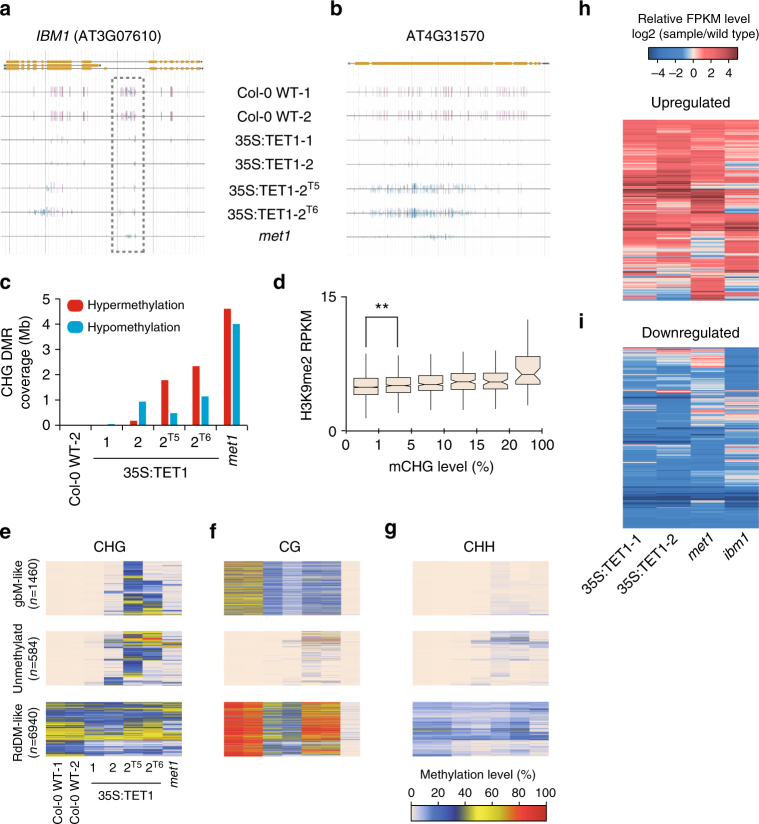
Fig. 2.
Global fluctuation of CHG methylation in 35S:TET1 plants. a Genome browser view of IBM1 (AT3G07610) in Col-0 WT, four 35S:TET1 transgenic plants, and met1. A decrease in CG methylation from coding regions was accompanied by an increase in non-CG methylation. Both CG and non-CG methylation were lost from the large intron (purple vertical lines = CG methylation, blue vertical lines = CHG methylation, and gold vertical lines = CHH methylation). b Genome browser view of a representative CHG hypermethylated region. c The amount of the genome affected by differential CHG methylation. These DMRs were defined relative to Col-0 WT-1, as Col-0 WT-2 DMRs were used to assess background interference. d Boxplot of H3K9me2 distribution in gbM loci (**t-test, p value <0.01). e Heat map of CHG methylation displaying CHG DMRs. Corresponding CG and CHH methylation levels are shown in f and g. Heat maps showing log2 transformed FPKM profiles of upregulated genes (h) and downregulated genes (i) in two 35S:TET1 transgenic individuals, met1, and ibm1 mutants relative to WT