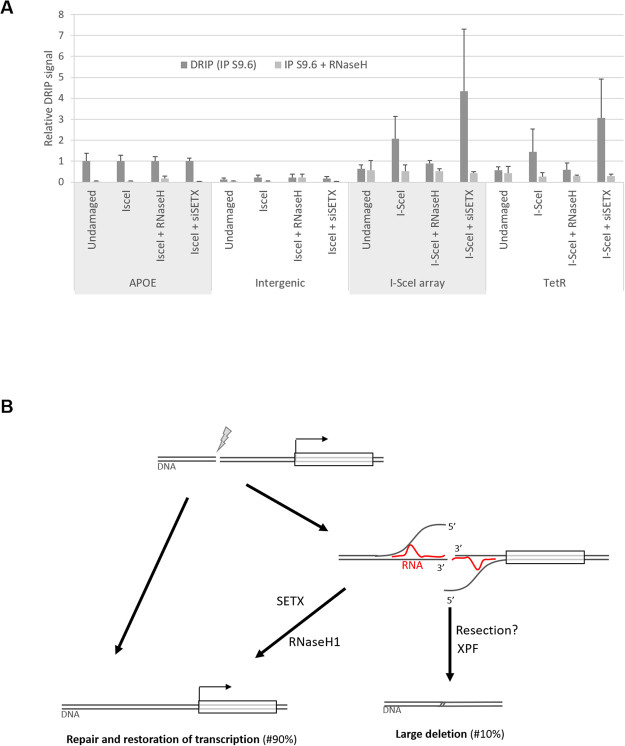
Figure 5.
DNA:RNA hybrids occur at the break site: (A) DRIP-qPCR analysis of DNA:RNA hybrid structure at TetR-IRES-NeoR gene in undamaged cells or after DSB induction. Primers targeting the APOE gene are used as a positive control for R loop formation, and primers specific to an intergenic region are used as a negative control. The values, corresponding to the signal following S9.6 IP of isolated DNA (dark grey bar) or of in vitro RNaseH-treated DNA (clear grey bar), are represented as fold increase normalised to the APOE positive control (Undamaged, n = 7 (from Fig. 4(F)); I-SceI, n = 7; I-SceI + RNaseH1, n = 3; I-SceI + siSETX, n = 4). (B) Model of DSB-induced large deletion dependent on a DNA:RNA hybrid associated with transcription from the DSB: Generally a DSB occurring in close proximity to a gene is efficiently repaired, either by HR or NHEJ, and the transcription program is not affected over the long term (left side). Alternatively (right side), transcription and DNA:RNA hybrid generation displaces the 5′ DNA strand. Senataxin is shown reversing this, promoting correct repair. ERCC1/XPF is required to cleave the displaced 3′ DNA strands.