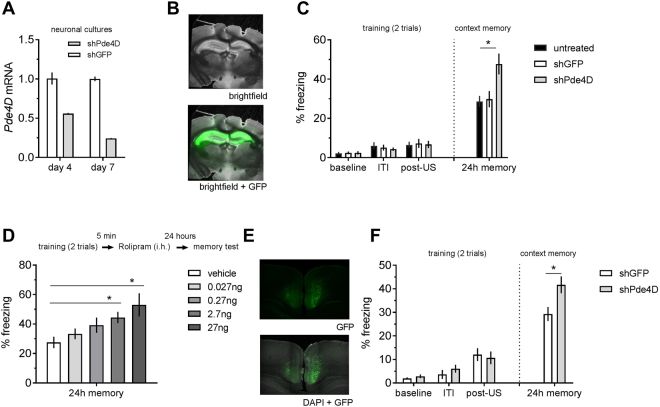
Figure 4.
Pde4d knockdown (KD) in HC and RSC enhances contextual memory. mRNA levels of Pde4d in hippocampal cultures treated with AAV5 expressing shPde4d or shGFP control. shRNA efficiently knocks down Pde4d mRNA levels in cultured neurons. (B) Stereotactic injection of AAV5 coexpressing the shRNAs and eGFP marker results in GFP fluorescence restricted to HC. (C) Freezing in the memory test but not during training (shown here as baseline - before first shock, inter trial interval (ITI) - between the two shocks, and post-US – after second shock) is significantly increased after Pde4d KD (n = 19) in HC as compared to control virus (n = 20) and uninjected mice (n = 32). (D) Posttraining intrahippocampal (i.h.) injection of the PDE4 inhibitor rolipram enhances contextual memory in a dose dependent manner (n = 25 vehicle, n = 8–16 drug, respectively). (E) Stereotactic injection of AAV5 carrying the shRNAs and expressing eGFP results in restricted fluorescence in rostral RSC. (F) Freezing in the memory test but not during training is significantly increased after Pde4d KD (n = 23) in RSC as compared to control virus (n = 24). Significant differences from shGFP (panel C/E) or vehicle (panel D) control are indicated by an asterisk (*).