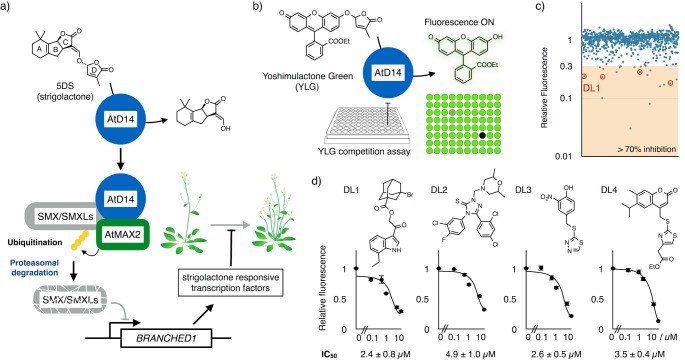
Figure 1.
Yoshimulactone-based chemical screening of D14 ligands. (a) Strigolactone signaling that suppresses shoot branching. (b) Schematic workflow of high-throughput screening for AtD14-ligand. (c) AtD14-binding activity of 800 compounds examined by YLG competition assay. The fluorescence intensities were measured after the incubation of YLG (1 μM) with AtD14 in the presence of library compounds (10 μM). Vertical axis indicates relative fluorescence normalized by no ligand control. Red circles indicate the four compounds that passed the second screening. (d) Chemical structure of the hit compounds and their inhibitory activity for D14-mediated YLG hydrolysis. Error bar indicates SE (n = 3 biological replicates).