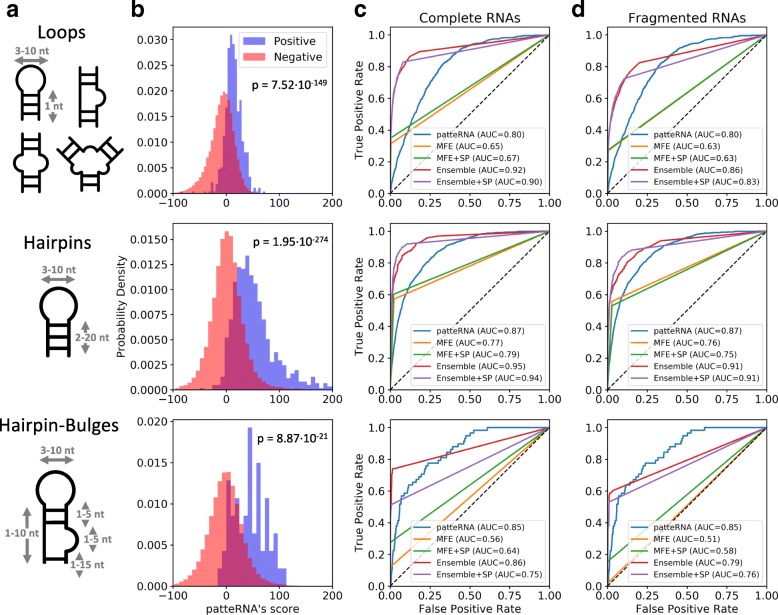
Fig. 3.
PATTERNA accurately detects canonical motifs in SHAPE data. The performances of five methods with the Weeks SHAPE data set are compared: PATTERNA, MFE structure prediction using NNTM (MFE), data-directed MFE structure prediction using NNTM (MFE+SP), Boltzmann ensemble sampling (Ensemble), and data-directed Boltzmann ensemble sampling (Ensemble+SP). a Schematic secondary structures of three scored motifs (loops, haipins, and hairpin-bulges). Allowed variations in loop and stem lengths are indicated by grey double arrows. bPATTERNA’s score histograms at regions where the tested motif was present (positive) or absent (negative) in reference structures. The p value corresponds to a one-sided Mann–Whitney U test between the two distributions. c, d ROC curves of performance of motif detection for each method when applied to complete (c) and fragmented (d) RNAs. The area under the curve (AUC) is reported in the legend. The dashed lines correspond to the performance expected from a random classifier. AUC area under the curve, MFE minimum free energy, NNTM nearest-neighbor thermodynamic model, ROC receiver operating characteristic, SP structure profiling