Fig. 4.
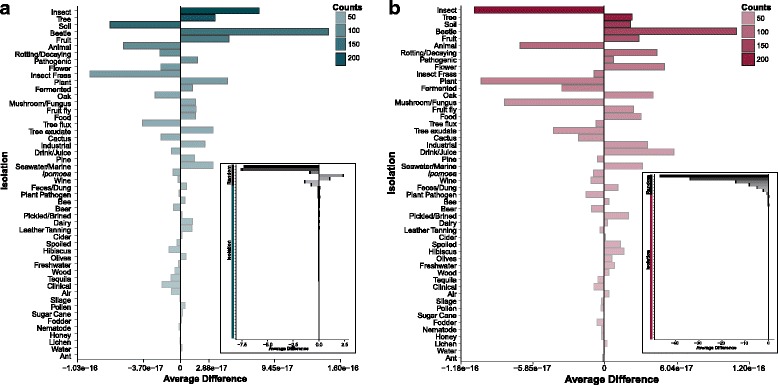
Isolation environments contribute to positive and negative associations among traits. We calculated the deviations for our observed data for both a positive and b negative associations. All of the deviations for the observed data were close to zero, suggesting that isolation environments contribute to the trait associations. The saturation of the bars represents sample sizes. In the insets, we removed the effect of the environment by randomly sampling species without regard to their environment for multiple sample sizes (4 ≤ n ≤ 217) and reproduced the environment data on the same scale for contrast (isolation versus random). Note that removing the effect of environment led to significant deviations from expectations for both positive (inset in a) and negative (inset in b) associations
