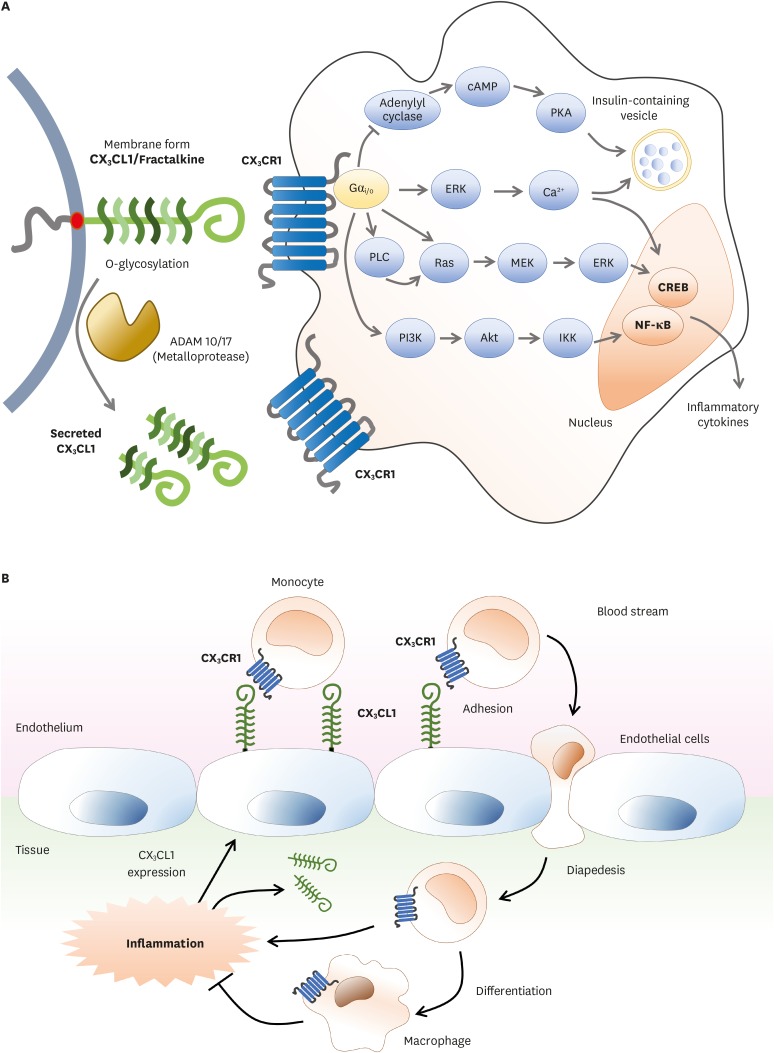
Figure 1.
CX3CR1-CX3CL1 signaling pathway and migration process of immune cells via their interactions. (A) CX3CL1/fractalkine, a transmembrane protein with O-glycosylated mucin-like stem, is expressed on the surface of immune cells and non-immune cells. Soluble forms of CX3CL1 can be made after proteolytic cleavage by metalloprotease ADAM 10/17. Both membrane bound and soluble forms of CX3CL1 can bind to CX3CR1. CX3CR1 is seven-transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor. The complex of CX3CL1-CX3CR1 can activate NF-κB or CREB signaling pathway which promotes the secretion of inflammatory cytokines. (B) CX3CL1 is expressed on the surface of endothelial cells near inflamed tissues. CX3CL1 induces chemotaxis to promote recruitment of CX3CR1 expressing immune cells. Monocytes flowing through blood stream will encounter and recognize CX3CL1 on the endothelium near inflamed tissues. As CX3CL1-CX3CR1 complex is formed, monocytes are ready to enter inflamed tissues and then enter diapedesis between junctions of endothelial cells. In this process, monocytes will undergo maturation and differentiate into macrophages. Mature macrophages can relieve inflamed conditions.
cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; PLC, phospholipase C; MEK, methyl ethyl ketone; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; IKK, IκB kinase; CREB, cAMP response element binding protein.