Figure 5.
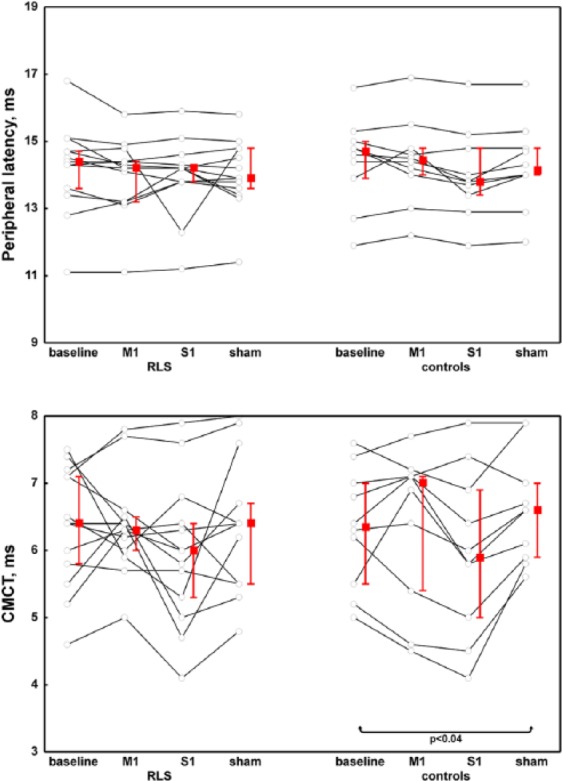
Peripheral latency of motor-evoked potential and the central motor conduction time in patients and controls with respect to the different stimulation modalities.
RLS, restless legs syndrome; M1, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over the primary motor cortex; S1, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over the primary somatosensory cortex; Sham, sham stimulation of M1; CMCT, central motor conduction time.
