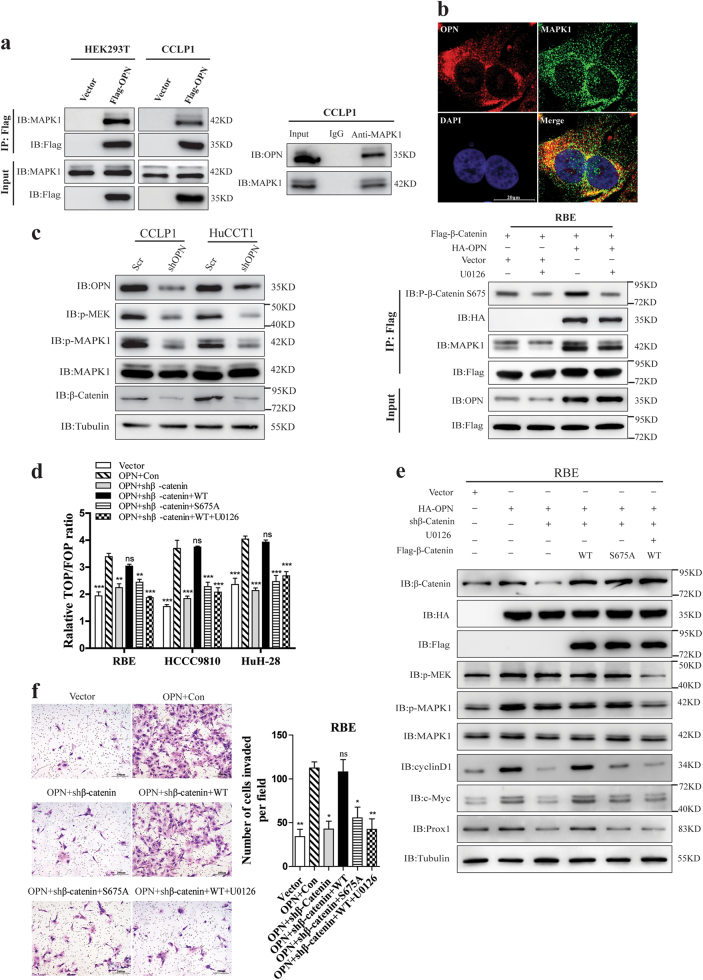
Fig. 7. OPN recruited and activated MAPK1 to promote β-Catenin S675 phosphorylation and ICC metastasis.
a Association of OPN with MAPK1 in HEK293T and CCLP1 cells. Interaction between exogenous OPN and MAPK1 in the left, CCLP1 cells and HEK293T cells was transfected with empty vector or Flag-OPN, total cell lysates was prepared for IP and IB using anti-FLAG or anti-MAPK1 antibodies. Endogenous MAPK1 in CCLP1 cells was determined by Co-IP with anti-MAPK1 monoclonal antibody, and rabbit IgG was used as nonspecific control. OPN was detected by anti-OPN antibody. b IF staining of OPN (red) and MAPK1 (green) in CCLP1 cells, Nuclei was stained with DAPI. c Knockdown of OPN in HuCCT1 and CLLP1 cells. IB examinations of both phosphorylated MEK (Ser217/221) and MAPK1 (Thr202/Tyr204) are shown in the left panel. RBE cells stably expressing Flag-β-Catenin were transfected with empty vector or HA-OPN and treated with 10 μM U0126 for 2 h, cell lysates were prepared, after that IP and IB were performed with anti-FLAG or specific antibodies indicated. The phosphorylation of β-Catenin S675 and OPN-MAPK1 complex was analyzed (right). d The TOP/FOP reporter plasmid was transfected and Luciferase reporter assays were performed in ICC cells. RBE, HCCC9810, and HuH-28 cells, with OPN or empty vector over-expressed and β-Catenin knockdown, were then rescued by wild-type β-Catenin (following U0126 treatment or not) or S675 mutants. e The activation of MEK/MAPK1 pathway and Wnt signaling pathway was determined with antibodies indicated. f Knockdown of β-Catenin could inhibit the invasion ability of CCLP1 cells induced by OPN, which could be restored by re-inducing β-Catenin-WT but not S675 mutants (S675A) or re-inducing β-Catenin-WT plus U0126 treatment. Scale bar = 20 μm