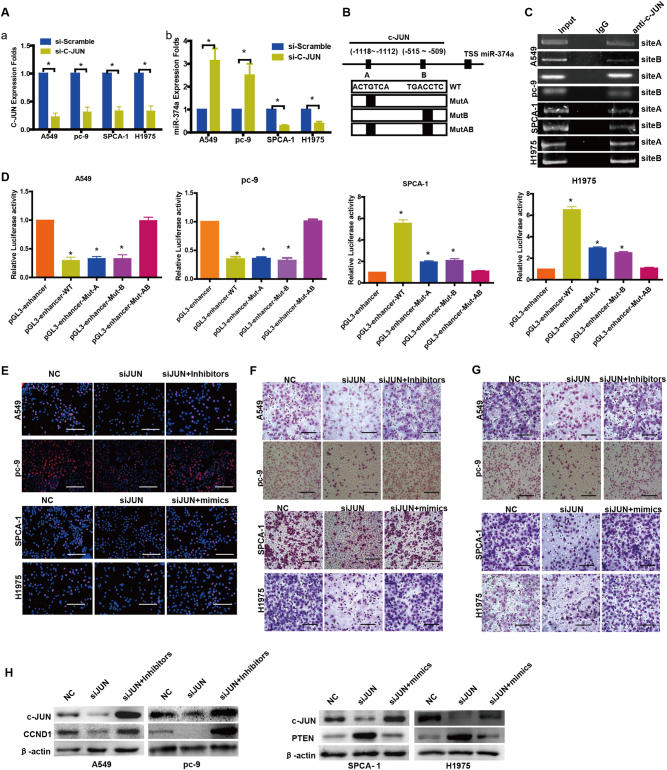
Fig. 5. c-JUN binds the promoter region of human miR-374a that mediates its effects on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in A549, pc-9, SPCA-1 and H1975 cells.
a (a) siRNAs were used to suppress c-JUN expression as shown by qPCR. a (b) Knocking down c-JUN respectively stimulated or inhibited expression of miR-374a in NSCLC cells. b Schematic representation of the promoter regions of miR-374a with putative c-JUN TFBSs (a, b) and the structure of the wild-type (WT) and TFBS mutant (MutA, MutB, and MutAB) luciferase reporters driven by the promoter. c ChIP assay using antibodies against c-JUN in NSCLC cells; PCR gel showing amplification of c-JUN-binding sites A and B. d Relative luciferase activity of the indicated promoter vectors in A549, pc-9, SPCA-1, or H1975 cells transfected with c-JUN plasmids. e EdU incorporation assays, f transwell migration assays, and g Boyden Chamber invasion assays of NSCLC cells were performed after transfection with NC, c-JUN siRNA, miR-374a mimics and/or inhibitors as indicated. Mean ± SD (n = 3). Scale bars, 100 μm. *P < 0.05. h Protein levels of CCND1 and PTEN were detected by western blot in NSCLC cells after transfection with NC, c-JUN siRNA, miR-374a mimics, and/or inhibitors