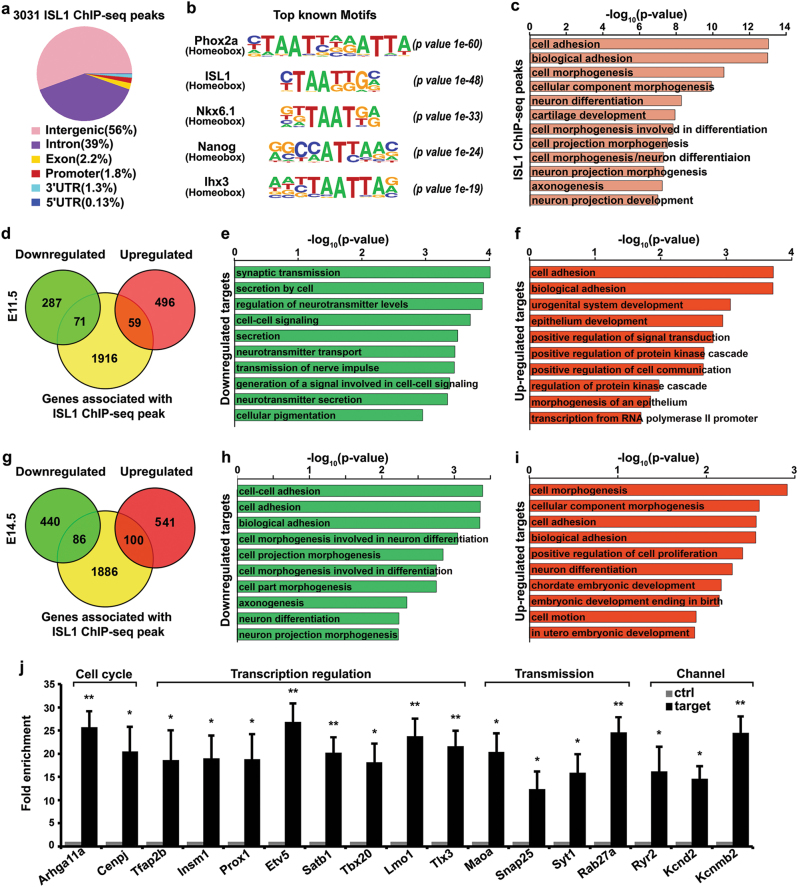
Fig. 8. ISL1 directly regulates a number of genes required for sympathetic neuron development.
a ChIP-seq ISL1-binding regions were mapped relative to their nearest transcription start site (TSS). Annotation includes whether a peak is in the TSS, transcription termination site, exon, 5ʹUTR, 3ʹUTR, intronic, or intergenic. b Top motifs enriched in the vicinity of ISL1-binding sites. c GO functional clustering of genes associated with ISL1 ChIP-seq peaks. d Overlay of ChIP-seq data and RNA-seq results from E11.5 Isl1 CKO sympathetic ganglia revealed 71 downregulated and 59 upregulated genes as potential direct targets of ISL1 in sympathetic neurons; p = 1.56 × 10−7, Fisher’s exact test. e, f GO functional clustering of these genes bound by ISL1 and downregulated (e) or upregulated (f) in E11.5 Isl1 CKO sympathetic neurons. g Intersection of ChIP-seq data and RNA-seq results from E14.5 Isl1 hypomorphic sympathetic ganglia revealed 86 downregulated and 100 upregulated genes as potential direct targets of ISL1 in sympathetic neurons; p = 4.6 × 10−13, Fisher’s exact test. h, i GO functional clustering of these genes bound by ISL1 and dysregulated in E14.5 Isl1 hypomorphic sympathetic neurons. j ChIP-qPCR validation of ISL1 binding at selected targets in E12.5–E14.5 sympathetic neurons, including those genes involved in the cell cycle, transcription regulation, neurotransmission, and ion channels. Error bars represent the s.d., n = 3, two-tailed t-test. *p < 0.05, or ** p < 0.01