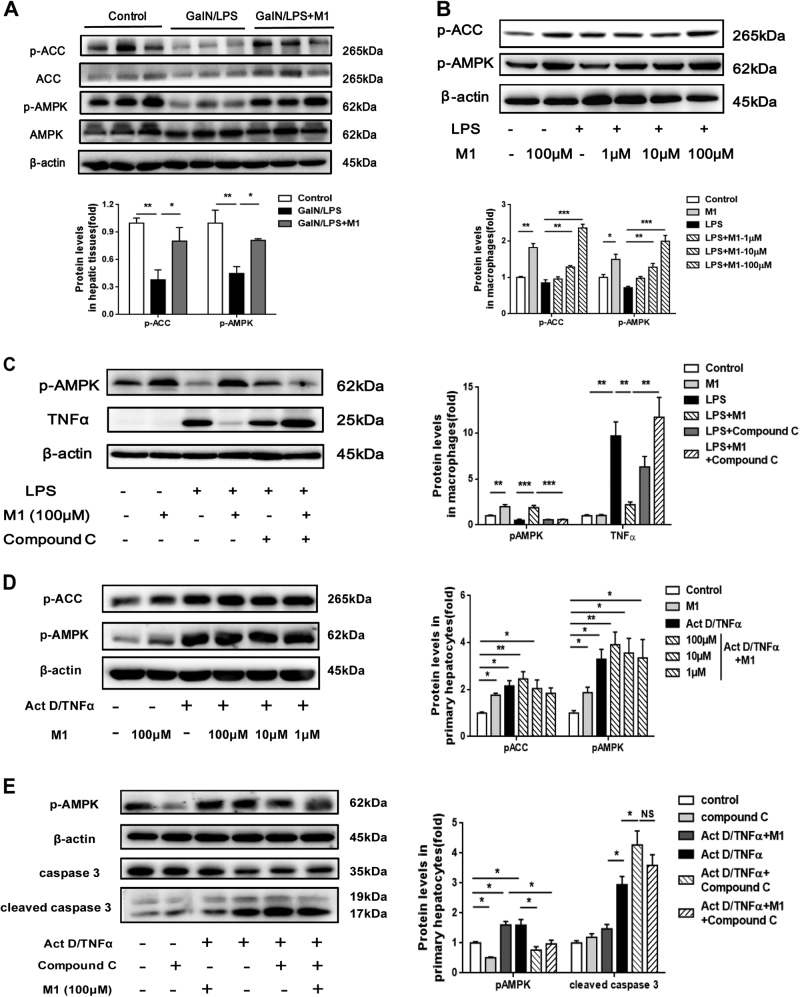
Fig. 5. AMPK is required for M1 exerting anti-inflammatory effect in macropahges and anti-apoptotic effect in hepatocytes.
a C57BL/6J mice were intraperitoneal injected either with vehicle or 30 mg/kg M1 every 8 h one time for three times. Liver tissues were collected at 4 h after GalN (400 mg/kg)/LPS (10 μg/kg) treatment. The hepatic levels of phosphor-ACC and phosphor-AMPK were measured by western blot. Statistical analysis was conducted for five pieces of liver tissues in each group. b The expression of phosphor-AMPK and phosphor-ACC in primary macrophages treated with different concentrations of M1 (1, 10, 100 μM) 1 h before the addition of 10 μg/ml LPS for 6 h, were analyzed by immunoblotting (n = 3). c The decreased expression of TNFα mediated by 100 μM M1 in LPS-treated macrophages were rescued by pretreatment of 25 μM Compound C for 1 h. Immunoblot analysis of phosphor-ACC and phosphor-AMPK protein expression were conducted (n = 3). d Primary hepatocytes were treated with different concentrations of M1 (1, 10, and 100 μM) 1 h before the addition of 0.1 μg/ml Act D and 10 ng/ml TNFα for 12 h. Immunoblot analysis of phosphor-ACC and phosphor-AMPK protein expression were performed (n = 3). e Primary hepatocytes were pretreated with 25 μM Compound C for 1 h in the presence or absence of 100 μM M1 and then treated with 0.1 μg/ml Act D and 10 ng/ml TNFα for 12 h. The expression of phosphor-AMPK, caspase 3, and cleaved caspase 3 were conducted (n = 3). Each value is mean ± S.E.M. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001