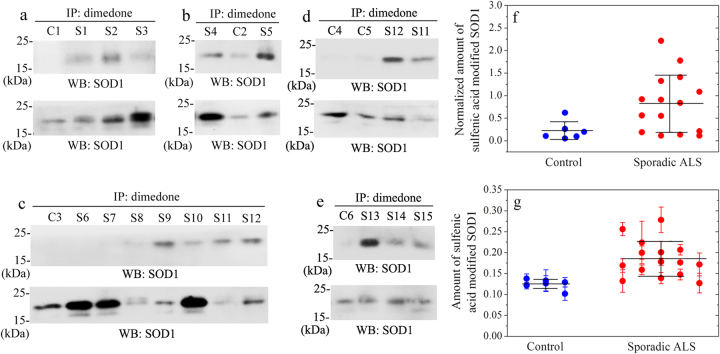
Fig. 7. Sulfenic acid-modified wild-type SOD1 level in cerebrospinal fluid of 15 sporadic ALS patients is significantly increased compared with 6 age-matched control patients (f: Western blot, F = 0.0207 and p = 0.021; g: ELISA, F = 0.0126 and p = 0.0019).
Two hundred microlitres of CSF samples were mixed with 2 μl of a cocktail protease inhibitors and 2 μl of 100 mM dimedone, immunoprecipitated with 1 μl of 1.0 mg/ml rabbit anti-dimedone polyclonal antibody overnight at 4 °C, and then incubated with 20 μl of Protein G Agarose beads for 12–14 h at 4 °C. The beads were washed thrice with PBS buffer, boiled in SDS-PAGE loading buffer without reducing agents for 5 min, and then probed with Western blot using mouse anti-SOD1 antibody (WB: SOD1, the upper lane (a–e)). Another 20 μl of CSF samples were boiled in SDS-PAGE loading buffer, probed with Western blot using rabbit anti-SOD1 antibody, and served as the input control (WB: SOD1, the lower lane (a–e)), which represented the total SOD1 content in CSF samples. Sulfenic acid modification of wild-type SOD1 was remarkably observed in CSF samples of 13 patients with sporadic ALS (S1–S5 and S8–S15, the upper lane (a–e)), but was not remarkably observed in those of 6 control patients (non-ALS patients) (C1-C6, the upper lane (a–e)) and 2 sporadic ALS patients (S6 and S7, the upper lane, c). Normalized amount of sulfenic acid-modified wild-type SOD1 in CSF samples of 15 patients with sporadic ALS (red solid circle, f) and 6 age-matched non-ALS control patients (blue solid circle, f) was calculated by the densitometry of sulfenic acid-modified wild-type SOD1 bands (WB: SOD1, the upper lane (a–e)), divided by that of the total SOD1 bands (WB: SOD1, the lower lane (a–e)). 100 μl of CSF samples were mixed with 1 μl of a cocktail of protease inhibitors and 1 μl of 100 mM dimedone, and added into each well of the ELISA plates coated with mouse anti-SOD1 antibody. The ELISA plates were incubated with 100 μl/well of 0.5 μg/ml rabbit anti-dimedone antibody followed by 100 μl/well of 1/10000 homologous goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase. Then 200 μl/well of the substrate 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine was added and the absorbance of the blue product was measured with a microplate reader at 630 nm. Amount of sulfenic acid-modified wild-type SOD1 in CSF samples of 15 sporadic ALS patients (red solid circle, g) and 6 age-matched non-ALS control patients (blue solid circle, g) was represented by the absorbance at 630 nm in each well. Data on absorbance with error bars were expressed as mean ± S.D. of 3 independent experiments (g). Statistical analyses were done using t-test. Values of p < 0.05 and p < 0.001 are considered as statistically significant and much significant, respectively