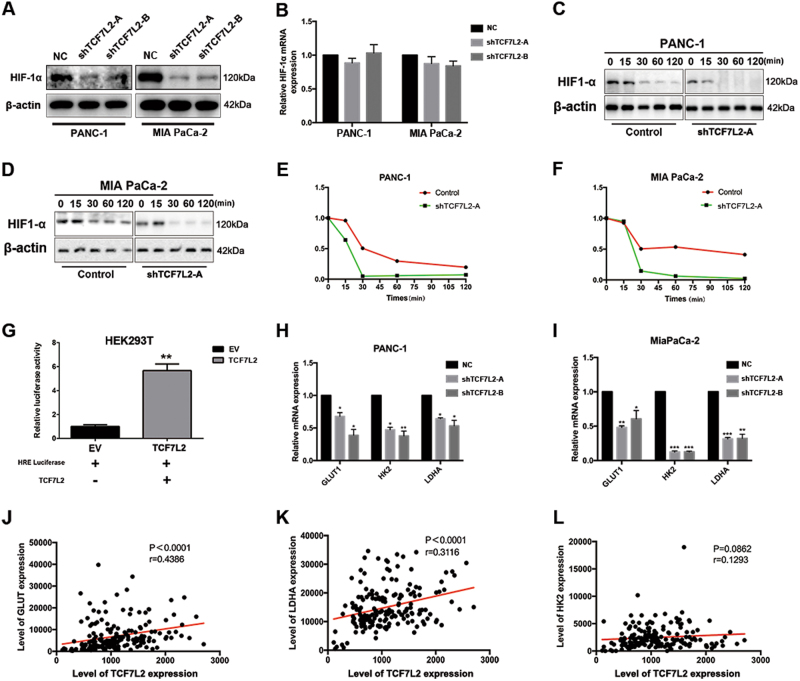
Fig. 4. TCF7L2 is positively correlated with HIF-1α stability and relevant glycolysis genes (GLUT1, HK2, LDHA) in pancreatic cancer.
a TCF7L2 silencing decreased the protein level of HIF-1α. b There was no significant change in the expression of HIF-1α at the transcriptional level in TCF7L2-silenced PANC-1 and MIA PaCa-2 cells. c–f Kinetics of HIF-1α protein degradation. HIF-1α protein degraded faster in shTCF7L2 cells than in controls in PANC-1 (c, e) and MIA PaCa-2 cells (d, f). g TCF7L2 could upregulate HRE-luciferase activity in HEK293T cells. **P < 0.01. h, i TCF7L2 silencing inhibited the expression of HIF-1α-targeted glycolytic genes, including GLUT1, HK2, and LDHA in PANC-1 and MIA PaCa-2 cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. control group. j, k TCF7L2 positively and significantly correlated with GLUT1 and LDHA expression in pancreatic cancer patients. l TCF7L2 positively correlated with HK2 expression, but this did not reach statistical significance