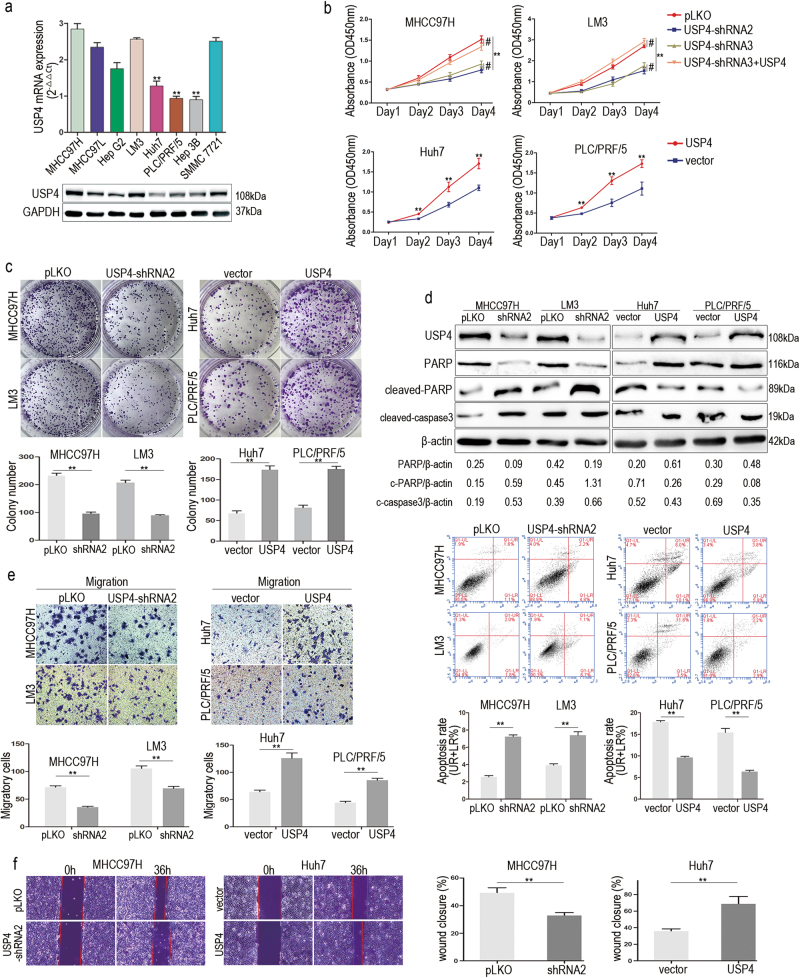
Fig. 2. High USP4 expression promoted HCC cells growth and migration in vitro.
a qRT-PCR and western blotting assays were used to detect the USP4 expression in eight HCC cell lines. The statistical analyses compared Huh7, PLC/PRF/5, and Hep3B cell lines with other HCC cell lines by using one-way ANOVA. b Cell proliferation in HCC cells with regulated USP4 expression was assessed by using CCK-8 assays. c Colony formation assays were performed in HCC cells with different levels of forced USP4 expression. The number of colonies was quantified. d Apoptosis in HCC cells with forced USP4 expression was assessed using FCM. UR+LR percentage represents the apoptosis rate. Western blotting assays were used to investigate expression of cell apoptosis indicator proteins. c-PARP, cleaved-PARP. c-caspase3, cleaved-caspase3. e The in vitro migration abilities of HCC cells with different forced USP4 expression were assessed using transwell assays. Representative images are shown. f Wound healing assays were performed to evaluate the migration of HCC cells with different forced USP4 expression. Cells were cultured in FBS-free medium in the experimental period and wound closure percentage was calculated. Each experiment was repeated three times. Error bars represent the SD. The statistical analyses compared the experimental group and the control group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and #P > 0.05