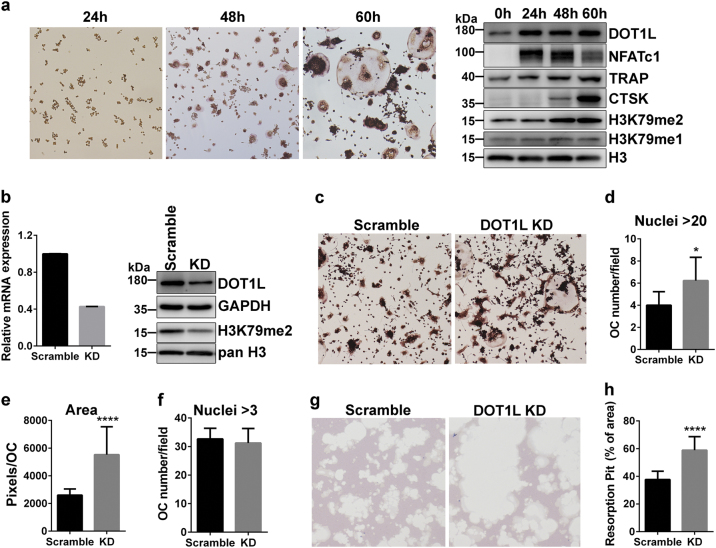
Fig. 1. Roles of DOT1L in OC fusion and resorption.
a Murine RAW264.7 cells stimulated with 10 ng/mL RANKL for the indicated time. TRAP staining (left panel) was performed and protein expression (right panel) of DOT1L, NFATc1, TRAP, CTSK, H3K79me1, and H3K79me2 in response to RANKL stimulation was detected by western blotting with specific antibodies. Total Histone H3 was used as a loading control. b RAW264.7 cells stably express scramble RNA or DOT1L shRNA collected for real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blot analyses. DOT1L mRNA and protein levels in DOT1L–knocked-down RAW264.7 cells are downregulated to half the levels in the control. H3K79me2 levels are significantly reduced in DOT1L–knocked-down RAW264.7 cells compared with the control. c Murine RAW264.7 cells stably express scramble RNA or DOT1L shRNA stimulated with 10 ng/mL RANKL for 60 h. Cells were fixed and stained using a TRAP kit. Representative images are shown. d–f OC number and surface area measurements are presented according to TRAP staining results shown in c. g Bone resorption assay: RAW264.7 cells stably express scramble RNA or DOT1L shRNA stimulated with 10 ng/mL RANKL for 5 days in osteoassay plates. Representative images of toluidine blue staining are shown. h Percentage of resorption area relative to the total area of the osteoassay plate calculated on the basis of staining results shown in g. Experimental data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation.*P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001, two-tailed unpaired t-test, compared with the scramble control