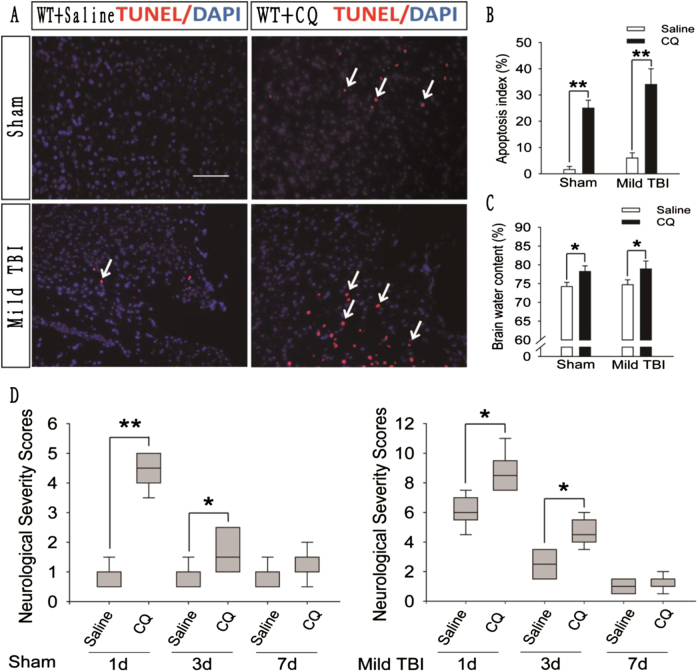
Fig. 4. CQ impairs autophagic flux in the injured cortex of WT mice after mild TBI and exacerbates the prognosis of brain injury.
a Images of apoptotic cells in cortical brain sections obtained from WT mice subjected to sham surgery or mild TBI that were administered CQ or saline. The results of TUNEL staining performed 1 day after sham surgery or mild TBI are shown. Arrows indicate TUNEL-positive cells. Scale bar = 50 μm. b Quantification of the number of TUNEL-positive cells in the cortical brain sections are shown in (a). The data are presented as means ± SEM, n = 5–6, **P < 0.01 compared to the control group. c Brain water content of WT mice 1 day after mice were subjected to sham surgery or mild TBI and then administered CQ or saline. The results were obtained using the wet–dry method. The data are presented as means ± SEM, n = 3, *P < 0.05 compared to the control group. d Neurological severity scores in WT mice subjected to sham surgery or mild TBI and then administered CQ or saline. Scores were obtained at 1, 3, and 7 days after sham surgery or mild TBI; the medians for all subjects are shown as the center line, the boxes represent the 25th–75th percentiles, and the lines show the range of the data, n = 7, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared to the control group at each time point