Fig. 6. Rapamycin favors autophagy resolution and reduces PrP90-231 intracellular accumulation.
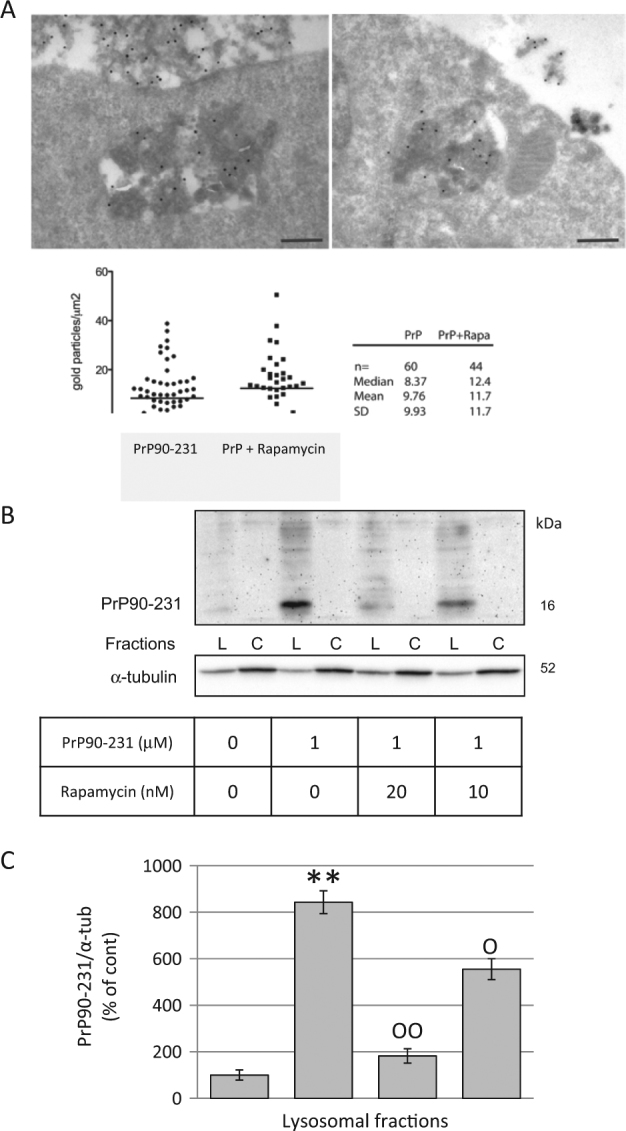
a A1 neurons treated with PrP90-231 (1 μM, 24 h) in the absence (upper- left panel) or presence (upper-right panel) of rapamycin (10 nM) were subjected to immunogold analysis for PrP90-231 aggregates into electron-dense cytoplasmic vesicles. The number of immunogold-positive spots have been counted and scored as ratio between the number of gold particles and vesicle area (gold particles/μm2). b After 24 hours of treatment with PBS, PrP90-231 1 mM or PrP90-231 in the presence of rapamycin (10 or 20nM), we separated crude lysosomal (Lys) and cytosolic (Cyt) fractions by differential centrifugation and performed immunoblotting using anti PrP90-231 antibody 3F4. The treatment with PrP90-231 caused a net increase of 16 kDa 3F4-immunioreactive band into the lysosomal fractions that was significantly and concentration dependently reduced by the presence of rapamycin. c PrP-immunoreactive bands in lysosomal fraction were quantified by densitometry and expressed as ratios on α-tubulin, from three separate experiments. The treatment with PrP90-231 caused a net increase of 16 kDa 3F4-immunoreactive band into the lysosomal fractions that was significantly and concentration dependently reduced by the presence of rapamycin. **P < 0.01 vs. cont; °P < 0.05, and °°P < 0.01 vs. PrP90-231. All data reported are representative of three independent experiments.
