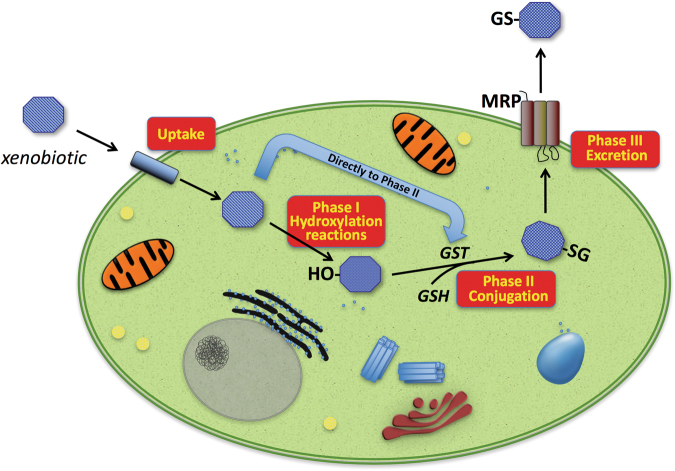
Fig. 2. Overview of enzymatic biotransformation of xenobiotics.
Harmful molecules may diffuse across the plasma-membrane and, inside cells, they may be targeted by the enzymes of the so-called Phase I metabolism. Main ones belong to the cytochrome P450 family, comprising several enzymes catalyzing different reactions including hydroxylation—the major reaction involved—oxidation and reduction. In the subsequent Phase II metabolism, the main role is played by GSTs that catalyze the conjugation of Phase I-modified xenobiotics to endogenous GSH. The conjugate obtained is then actively transported out of the cell by different transmembrane efflux pumps (Phase III). Some compounds may enter Phase II metabolism directly