Fig. 2. A simplified food web that includes Aedes and its predators in the aquatic and terrestrial environment.
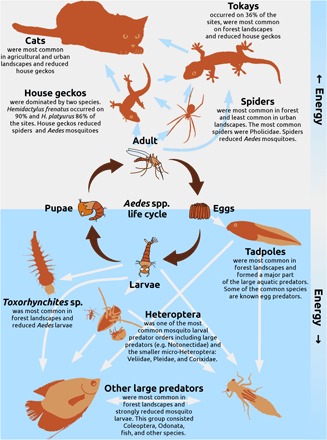
Blue and white arrows show the direction of energy flow from prey to predator. In the center of the figure, the life cycle (dark brown arrows) of Aedes shows that adult female mosquitoes lay eggs, which develop into larvae that will pupate, after which adult mosquitoes will emerge. In these different life cycle stages, Aedes spp. are exposed to different predators in the terrestrial (upper gray area) and aquatic (lower blue area) environments.
