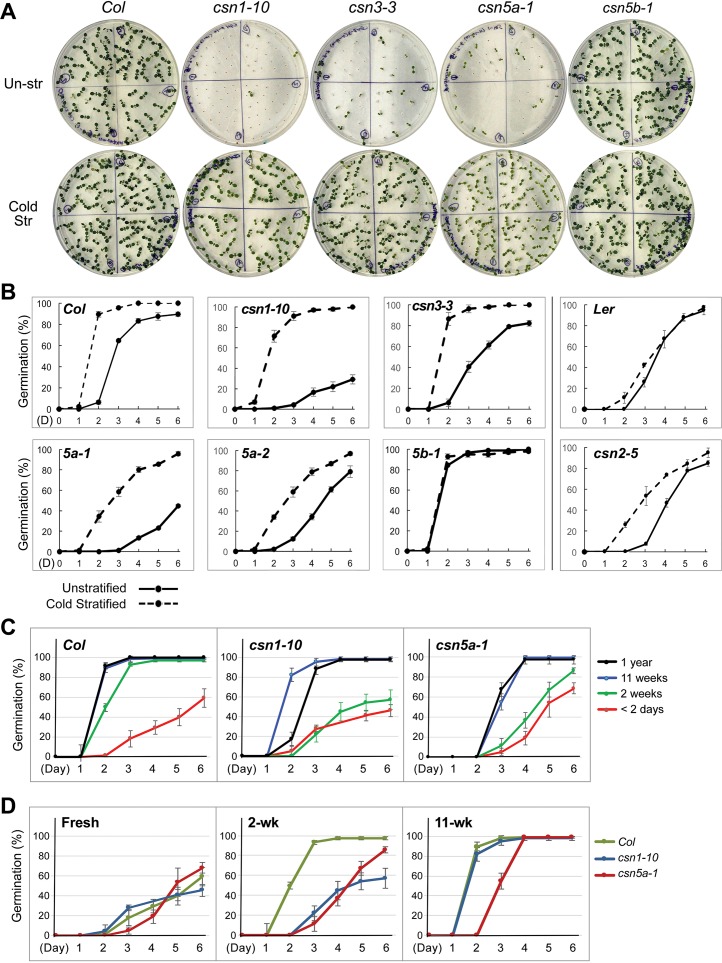
Fig 2. Seed germination phenotype of the csn mutants.
(A) Representative images showing seed germination status of indicated mutants. Seeds were cold stratified for 4 days (Cold Str) or had not stratified (Un-str). Photographs were taken at day 6. (B) Germination rates of unstratified (solid lines) or cold stratified (broken lines) seeds of the csn mutants. csn5a-1, csn5a-2, csn5b-1, csn1-10, csn3-3 were compared to Col wild type, while csn2-5 to Ler wild type. With the exception of csn5b-1, all other csn mutants tested exhibited slower and lower germination rates compared to Col, when not cold stratified. (C) Germination rates of Col, csn1-10 and csn5a-1 seeds that had been in dry storage for indicated period of time. csn1-10 and csn5a-1 seeds required extended after-ripening time than Col to release dormancy. csn5a-1 additionally showed delayed germination. (D) Germination rates of freshly collected, partially after-ripened (2 weeks), or fully after-ripened (11 weeks) seeds of Col, csn1-10, and csn5a-1. The germination deficiency of csn1-10 and csn5a-1 were most readily observed with the seeds of two weeks after seed-collection. csn5a-1 seeds exhibited a delay in germination even in fully after-ripened seeds. In all panels, error bars represent standard deviation from 4 repeats (n = 4). See also S2 and S3 Figs.