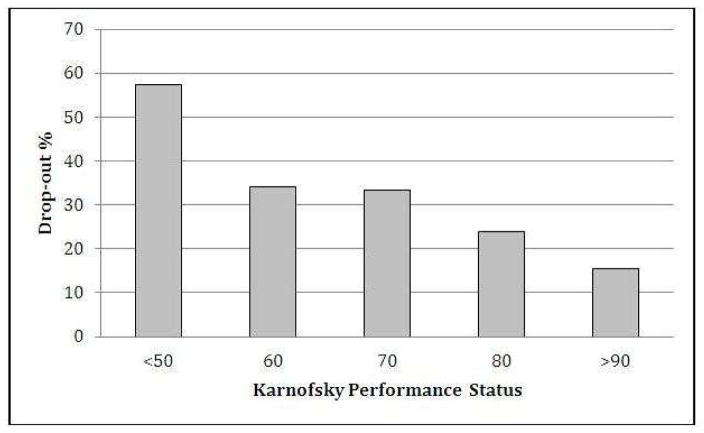
Figure 1. Association between Karnofsky Performance Status and Attrition.
Considering KPS as a categorical variable, we estimated the odds of dropping out from the study using KPS >90 as baseline. The OR (95% CI; p-value) for each category were: KPS=80: 1.73 (.90–3.31; .1) / KPS=70: 2.75 (1.48–5.13; .001) / KPS=60: 2.82 (1.48–5.40; .002) / KPS<50: 7.36 (3.80–14.29; <.001). We also estimated the odds of dropping out from the study by KPS, assuming that KPS was a continuous variable: OR 1.55 (1.35–1.76;p <.001) per 10 points decrease in the KPS score.