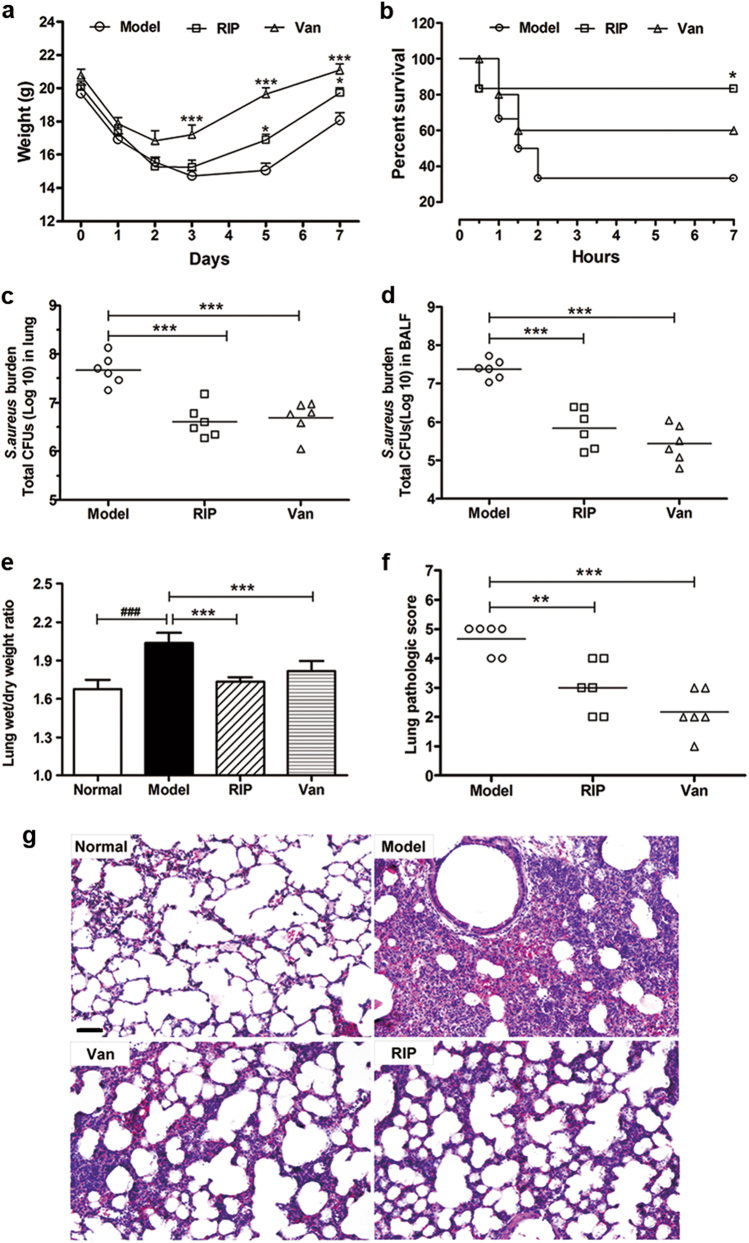
Fig. 1. LAC-infected pneumonia mice were protected by blocking the agr system.
a The body weight of LAC-infected mice recovered after treated by 20 mg/kg RIP or 10 mg/kg vancomycin (n = 7). b Survival of BALB/c mice nasally inoculated with LAC (3 × 107 CFU) and treated with PBS, RIP, or vancomycin by i.p. injection at 1 and 6 h after infection (n = 12). c, d The number of CFU in the lung (c) or in the BALF (d) was calculated from the number of colonies growing on plates (n = 6). e Effects of RIP on lung injury in LAC-infected mice were analyzed by Lung wet/dry weight (n = 6). f After 24 h infection, the left lung of infected mice were harvested, fixed, stained with HE, and analyzed microscopically. The total pathologic score for each mouse was calculated. Severity was graded on a scale of 0–5, with 0 representing normal lung and 5 representing severe pneumonia (n = 6). g Lung histopathologic examination of LAC-induced pneumonia 24 h after bacterial challenge in mice. The original magnification is ×200. The bar length represents 50 μm. Data were shown as mean (c, d, f), mean ± SD (e), or mean ± SE (a). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0001 vs. model group; ###P < 0.0001 vs. normal group