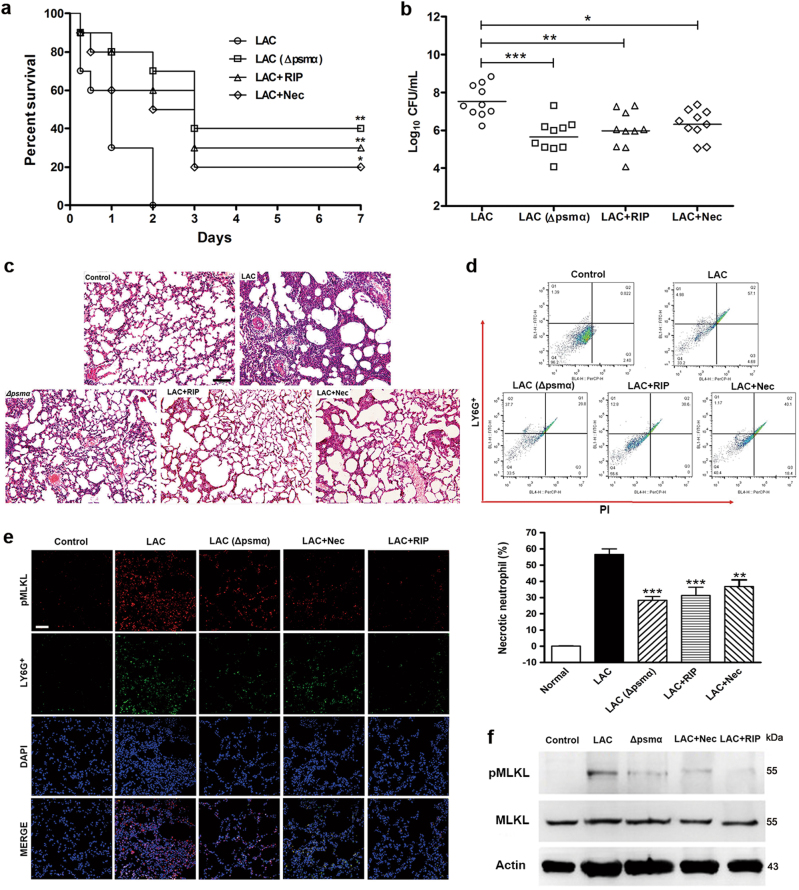
Fig. 7. Inhibiting necroptotic cell death protects the infected mice.
BALB/c mice nasally infected by 5 × 107 CFU LAC were treated by 20 mg/kg RIP or 15 mg/kg Nec at 1 and 6 h after infection. Or BALB/c mice infected by 5 × 107 CFU ∆psmα. a The survival rate of infected mice (n = 10). b After infection 24 h the bacterial CFU in the lung cultures were quantified (n = 10). c After 24 h infection, the lung of mice was harvested, fixed, stained with HE staining, and analyzed microscopically. The original magnification is ×200. The bar length represents 50 μm. d Flow cytometry was used to analyze the proportion of necrotic neutrophils in lung tissues of BALB/c mice after infection 24 h (n = 6). e Immunofluorescence microscopy is used to localize the pMLKL in the lung tissue of BALB/c mice in different groups. The bar length represents 50 μm. f Levels of pMLKL, MLKL, and β-actin in neutrophils isolated from bronchoalveolar lavage of BALB/c mice were detected. Data were shown as mean (b) or as mean ± SE (d). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0001 vs. LAC-infected group