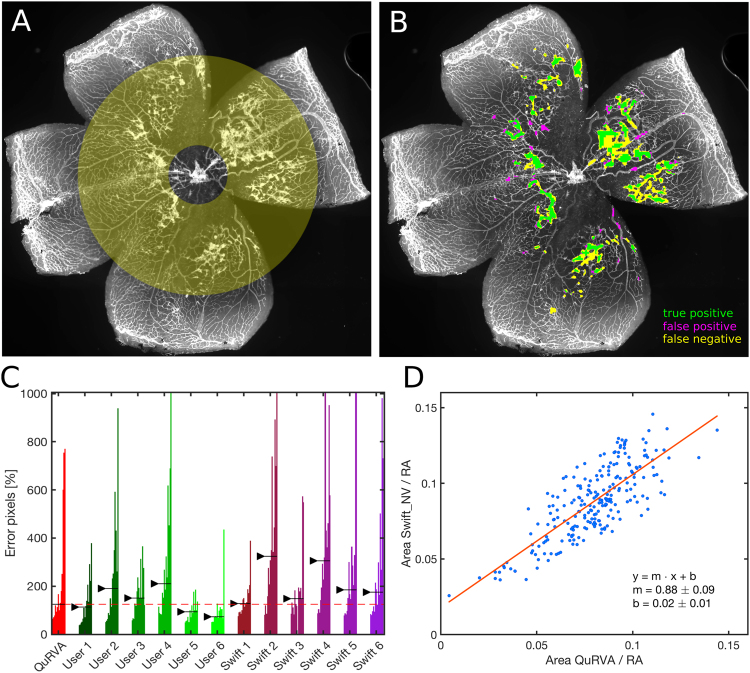
Figure 3.
Segmentation performance of QuRVA. (A) Original image of a lectin-stained flat-mounted retina, where the region considered for analysis is enhanced in yellow. (B) QuRVA segmentation overlapped with original image indicating agreement and disagreement with manual segmentation consensus. (C) Relative error of all methods grouped by user. The total error is defined as the number of false positive plus false negative pixels, using the consensus as ground truth, and displayed as a percentage of the consensus pixels per image. The median relative error across images for each method is indicated with a black arrow. The median error of QuRVA is better than three of the six manual segmentations and is better than all swift segmentations, independently of the operator. The vertical scale has been adjusted to fully fit 97% of the bars in the plot. (D) Correlation between Tufts areas computed by SWIFT_NV and QuRVA, normalized by the whole retina area (RA) from a set of 272 C57BL/6 J OIR images. For this computation, the image set used to train the model was enlarged by adding 50 images segmented with SWIFT_NV by only one user to the original set of 14 images. Pearson correlation coefficient is R = 0.79 (p = 10−50). The inset describes the fit results where both the slope (m) and the y-intercept (b) are displayed along with the 95% confidence range.