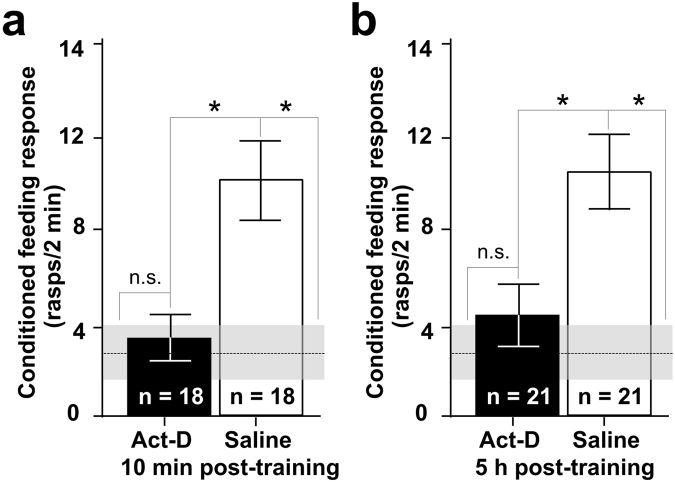
Figure 4.
LTM at 24 h is dependent on transcription in both the early and a later stage of memory consolidation after single-trial learning. (a) Treatment with Act-D at 10 min post-training reveals that transcription is required for 24 h LTM during the early stage of memory consolidation, around 1 h after single-trial classical conditioning. (b) Treatment with Act-D at 5 h post-training reveals that transcription is also required for LTM during a later stage of memory consolidation, around 6 h after single-trial classical conditioning. Means and standard errors are shown for the drug and saline treated groups. The mean non-treated naive baseline level of the feeding response to amyl acetate (n = 20 animals) is indicated by the dashed line with the gray band showing the standard error. Asterisks indicate significant differences revealed by multiple post-hoc tests. Test statistics for data in a: One-way ANOVA, p < 0.001; Tukey’s tests, Saline versus Act-D and baseline, both p < 0.01, Act-D versus baseline, p > 0.05 (not significant, n.s.). Test statistics for data in b: One-way ANOVA, p < 0.0007; Tukey’s tests, Saline versus Act-D and baseline, both p < 0.01, Act-D versus baseline, p > 0.05 (n.s.).