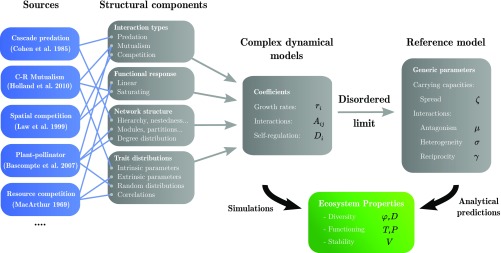
Fig. 1.
General outline of our approach. On the left are listed examples of sources from the literature (18–22), from which model features have been extracted (see full list in SI Appendix, Numerical Experiments). Diverse combinations of these model features and variations of their parameters yield distinct communities, characterized by the coefficients and functional response in the dynamics Eq. 1. We simulate them until they reach an assembled equilibrium, whose properties we measure. We then randomize interactions and carrying capacities, preserving the four statistics in Eq. 3. The randomized community’s equilibrium properties are known analytically from the solution of the reference model (6) and can be compared with simulation outcomes; see Fig. 2.