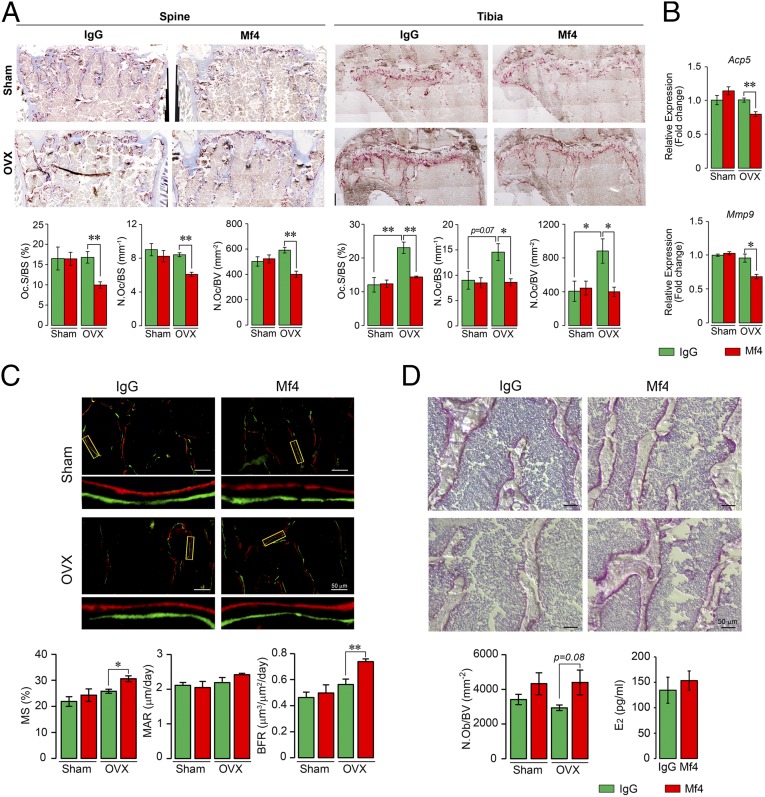
Fig. 4.
Monoclonal anti-epitope FSHβ antibody Mf4 reduces bone resorption and stimulates osteoblastic bone formation. The vertebral column (spine) and tibia from the mice above (Fig. 3C) were dissected and processed for Acp5 staining. Shown are representative images of Acp5-stained sections from vertebral column (spine) and tibial head (tibia), with parameters of resorption, namely Oc.S/BS, N.Oc/BS, and N.Oc/BV (A). mRNA expression (qPCR) for Acp5 and Mmp9 in marrow-derived osteoclasts obtained from these mice showed reduced osteoclastogenesis in the Mf4-treated group (B). These mice were also injected with calcein and xylelol orange 5 d apart before sacrifice, and bones were processed for dynamic histomorphometry and alkaline phosphatase staining of osteoblasts. Shown are fluorescent micrographs of vertebral column displaying xylelol orange (red) and calcein (green) labels, and estimates of MS, MAR, or interlabel distance, and BFR (C). Alkaline phosphatase-labeled sections and calculated N.Ob/BV are shown (D). Statistics: n = 5 mice per group; for B, n = 3, technical replicates; mean ± SEM; two-tailed Student’s t test, corrected for multiple comparisons; *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, or as shown.