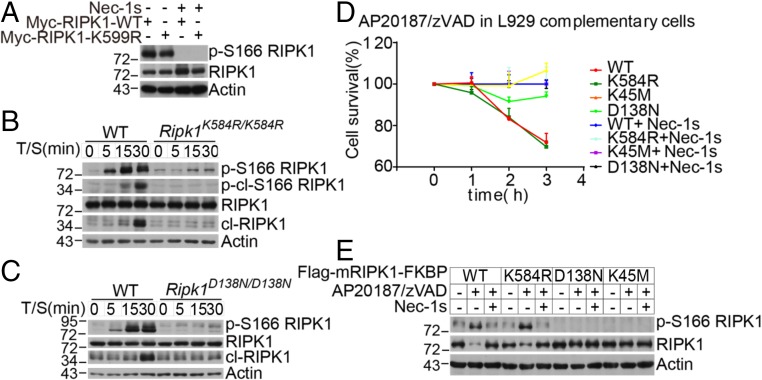
Fig. 4.
The RIPK1 K584R mutation does not directly block RIPK1 kinase activity. (A) RIPK1 KO 293T cells were transfected with Myc-tagged RIPK1 WT or K599R in the absence or presence of 10 μM Nec-1s. The cell lysates were collected 24 h after transfection and analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (B and C) WT and Ripk1K584R/K584R (B) and WT and Ripk1D138N/D138N (C) immortalized MEFs were pretreated with 100 nM SM-164 2 h and then treated with 100 ng/mL TNFα for 5, 15, and 30 min. The cells were lysed with 0.5% Nonidet P-40 buffer and analyzed by Western blotting analysis of p-S166 RIPK1 and RIPK1 antibodies as indicated. (D and E) RIPK1 KO L929 cells were infected with retrovirus encoding Flag-tagged mRIPK1 WT-FKBP, K584R-FKBP, K45M-FKBP, and D138N-FKBP by the Tet-On Advanced Inducible Expression System. RIPK1-reconstituted L929 cells were treated with 1 μg/mL doxycycline for 48 h to induce the expression of RIPK1. The cells were then pretreated with 10 μM Nec-1s for 30 min and then treated with 1 nM AP20187 and 50 μM zVAD.fmk. The cell survival was measured with CellTiterGlo (D). The RIPK1 kinase activity was analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies (E).