Fig. 5.
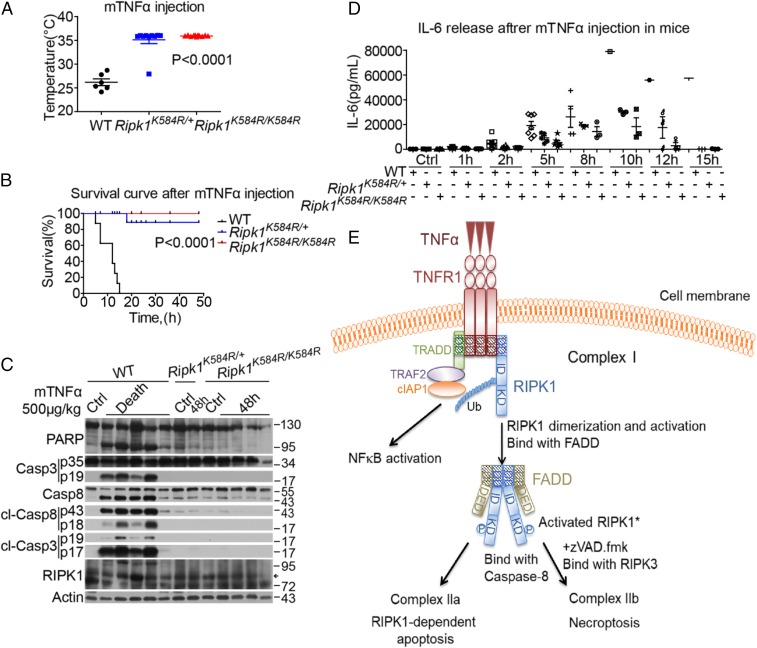
Ripk1K584R mice are protected against TNFα-induced SIRS. (A) Body temperatures of 6 male WT, 10 male Ripk1K584R/+, and 11 male Ripk1K584R/K584R mice (6–8 wk old) were measured 10 h after i.v. injection with 500 μg/kg mTNFα (∼10 μg/mouse). (B) Survival curves of 8 male WT and 9 male Ripk1K584R/+ and 12 male Ripk1K584R/K584R mice (6–8 wk old) injected with mTNFα intravenously. (C) Five WT, one Ripk1K584R/+, and four Ripk1K584R/K584R mice (8–10 wk old) were injected with mTNFα. A WT mouse, a Ripk1K584R+ mouse, and a Ripk1K584R/K584R mouse (8–10 wk) were injected with vehicle PBS as control. Thymi were harvested from five WT mice immediately after they died from mTNFα injection, or from other mice 48 h after injection. The tissues were lysed and analyzed by Western blotting with corresponding antibodies. (D) Serum concentrations of IL6 were demonstrated using ELISA after mTNFα injection at the indicated time points. Eight male WT, six male Ripk1K584R/+, and seven male Ripk1K584R/K584R mice (6–8 wk old) were analyzed. (E) Model showing that, in cells stimulated by TNFα, RIPK1 is rapidly recruited into TNFR1 with TRADD, TRAF2, cIAP1/2, etc., to form complex I, which exists for 5–15 min. During the transition of complex I to complex II, RIPK1 undergoes dimerization, which leads to its activation. Activated RIPK1* then binds to FADD. In apoptosis-competent cells, the RIPK1*/FADD complex in turn binds to caspase-8 (complex IIa) to mediate caspase activation and apoptosis. When caspase-8 fails to be activated, the RIPK1*/FADD/caspase-8 complex binds with RIPK3 to form complex IIb, which executes necroptosis by mediating the activation and oligomerization of MLKL.