Figure 7.
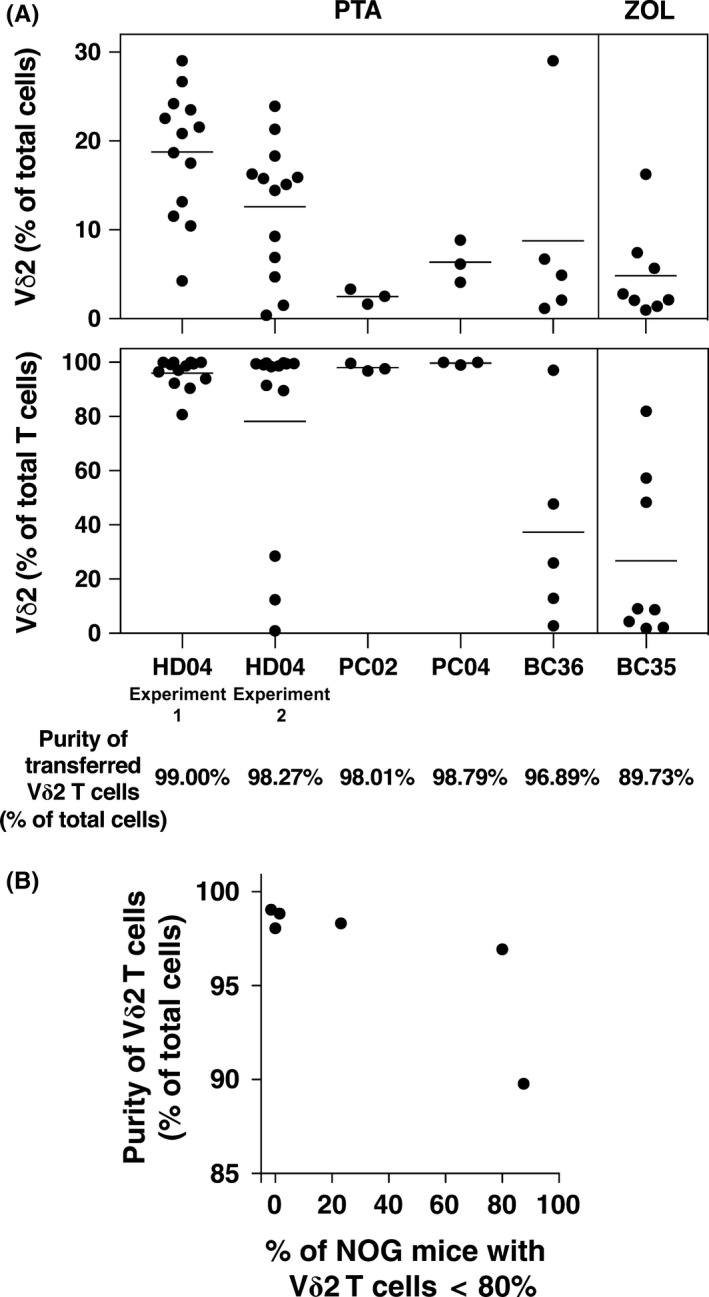
Purity of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells helps to determine their engraftment success after adoptive transfer in NOG mice. A, Summary of the results of NOG mouse engraftment with expanded Vγ2Vδ2 T cells. Top panel: Levels of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells as a percentage of total cells for each transfer experiment. Bottom panel: Levels of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells as a percentage of T cells for each transfer experiment. Each point represents 1 NOG mouse. Vγ2Vδ2 T cells were expanded using PTA except for BC35 that was expanded using Zol. Thawed Vγ2Vδ2 T cells were used for cells derived from cancer patients whereas freshly expanded Vγ2Vδ2 T cells were used for the healthy donor. The purity of the starting populations as a percent of total cells is listed at the bottom. B, Purity of the starting population of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells helps to determine engraftment success. The purity of the transferred Vγ2Vδ2 T cells is correlated with the percentage of NOG mice with predominant Vγ2Vδ2 T cell populations (>80%) at 2 weeks. Each data point represents 1 transfer experiment
