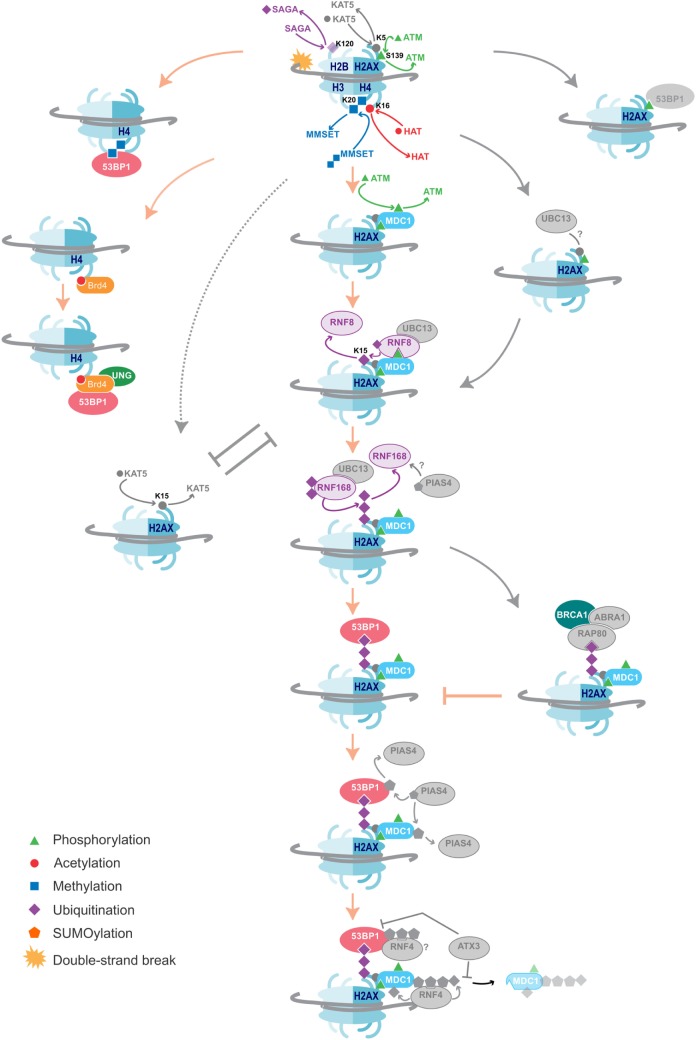
Figure 2.
DNA damage repair pathways dictate class-switch recombination (CSR) efficiency. An overview of the histone modifications, and the writers and readers associated with them that are essential for CSR, as well as suggestions of additional likely factors. Color = confirmed in NHEJ and CSR, Gray = DNA damage repair factors not yet shown to affect CSR. The key proteins and histone modifications that have been shown to be essential for resolving the DNA double-strand breaks in CSR are summarized. A common theme is the recruitment of 53BP1, which is essential for efficient repair and isotype switching. Importantly, these repair pathways also function in NHEJ. Additional DNA damage repair proteins and histone modifications that have not yet been shown to play a role in CSR are indicated in gray. Some proteins and histone marks involved in other repair pathways, such as homologous recombination (HR), are also indicated in the figure. As these pathways inhibit the NHEJ pathways, they may provide negative control of CSR. Indeed, knockdown of BRCA1 has been shown to increase isotype switching efficiency.