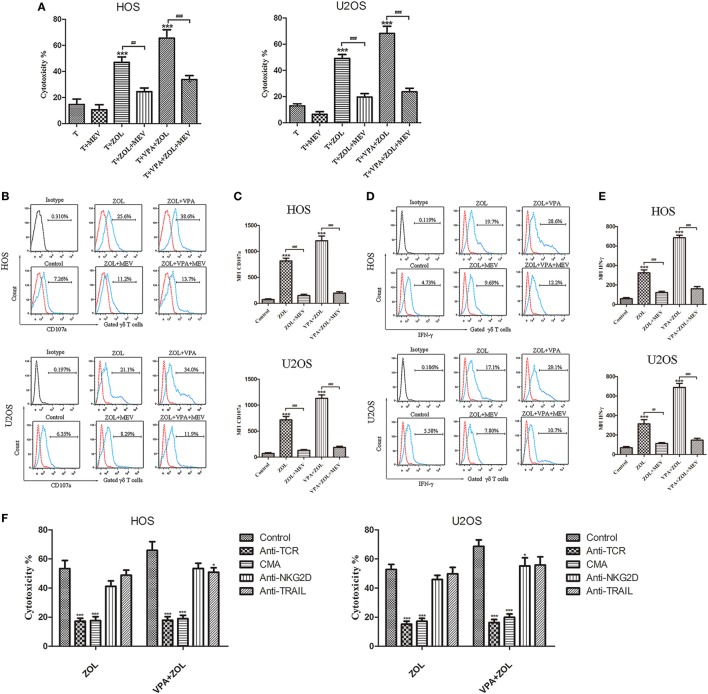
Figure 4.
Mechanisms of the antitumor efficacy of γδ T cells induced by valproic acid (VPA) and zoledronate (ZOL). Osteosarcoma cells were pre-treated with 5 µM MEV 1 h prior to incubation with control or VPA or/and ZOL for 24 h. Then tumor cells were co-cultured with γδ T cells for 2 h at an E:T ratio of 5:1. (A) γδ T cells cytotoxicity against osteosarcoma cells was determined by MTS assay. The cytotoxic effect of γδ T cells induced by VPA and ZOL could be significantly inhibited by MEV (B,C) CD107a expression levels were evaluated by flow cytometry. MFI of CD107a+ γδ T cells was presented in histograms. (D,E) IFN-γ expression levels were evaluated by flow cytometry. MFI of IFN-γ+ γδ T cells was presented in histograms. (F) γδ T cells cytotoxicity was significantly inhibited in the presence of blocking Abs against TCR or concanamycin A (CMA), and partly reduced by blocking NKG2D or TRAIL. Red histogram line was isotype control and panels were overlapped. All the values were shown as mean ± SD from three separate experiments; *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 versus control [T in (A)], ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001.