Figure 3.
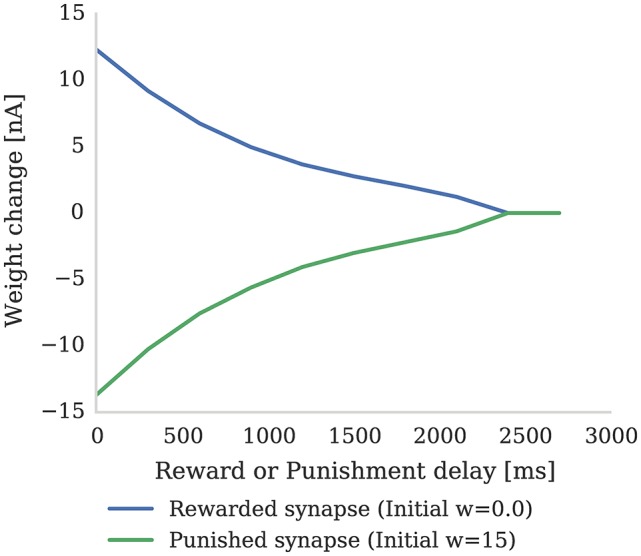
The strength of a single synapse after delayed reward and punishment. Each data point represents a separate experiment with a single pre-synaptic neuron connected to two post-synaptic neurons. A single pre-synaptic spike at time 1 ms is fired which causes both post-synaptic neurons to fire at time 3 ms. A single dopaminergic spike with Dc = 0.1 for reward and Dc = −0.1 for punishment is fired at different times between 4 and 3,000 ms. All the parameters are set to the values shown in Tables 1, 2. It can be seen that the longer dopamine is delayed, the more the eligibility trace decays and thus the smaller the resultant weight change. When the eligibility trace decays to zero at around 2,400 ms, the synapses are no longer affected by dopamine release.
